In modern manufacturing, choosing the right material for your project is essential in building efficient, yet long-lasting products. Now, this is where bar stock and plate stock come in. They are among the most used raw materials; each comes paired with its strengths and limitations. While both are staples in the precision manufacturing industry, understanding the difference between them will help you make smarter choices.
In this article, we are going to discuss bar stock vs plate stock: characteristics, benefits, and practical industrial applications.
Introduction: What is Bar Stock?
Bar stock is a solid raw material available in multiple shapes and sizes. It is frequently found in round, rectangular, and square shapes. However, it is particularly preferred in the precision manufacturing and machining industries.
It has a consistent structure throughout its length. It is ideal for operations like cutting, drilling, grinding, and milling. Bar stock also comes in a variety of materials such as aluminum, stainless steel, and plastic. Thus, it allows you to individually tailor and produce precise, accurate parts.
Bar Stock: Commonly Found Types and Frequent Usage
Bar stock comes in a variety of materials, each built to meet certain requirements of the manufacturing industry.
The following are some of the common types of Bar stock:
-
Aluminium Bar Stock:
Aluminium has high thermal conductivity and excellent corrosion resistance. However, its lightweight properties are what make it stand out. It is widely used in industries like aerospace and electronics, where lightweight components are a must-have.
-
Carbon Steel Bar Stock:
Carbon steel is among the most economical, durable, and stable metals. It is easy to handle and easy to weld. This makes it ideal for parts having to bear high stress, such as shafts and gears. Thus, it is a staple in the aeronautical and transportation industries.
-
Plastic Bar Stock:
Plastic bar stocks are a non-metal alternative for industries that require non-conducting and chemical-resistant parts. It suits well in industries such as pharmaceuticals and food processing.
Bar stocks also come in different shapes and sizes: cylindrical rods, for example, are useful in turning processes. Flat bars, however, aid in making components that need structural stability. Square-shaped bars are used in the production of frames and brackets. Essentially, in the machining industry.
Introduction: What is Plate Stock?
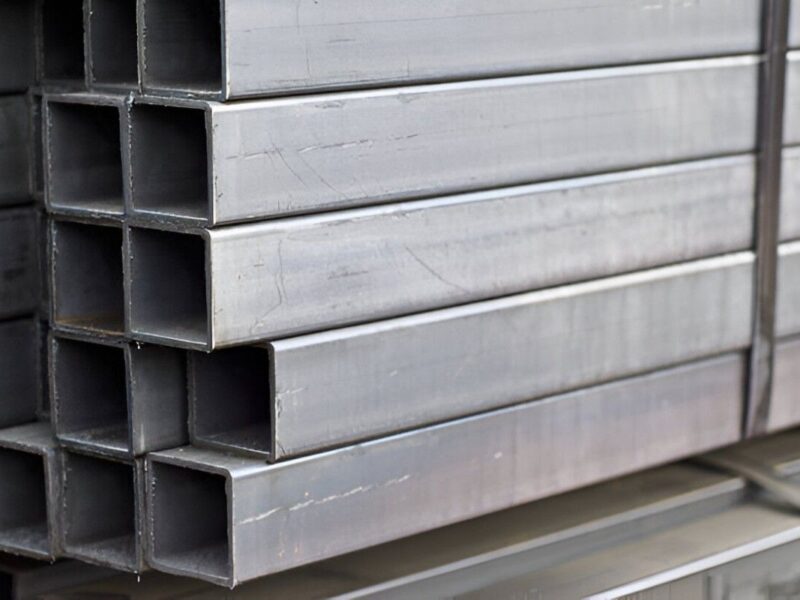
Plate stock is a flat, solid sheet of metal that is used as a raw material in a wide range of industrial and structural applications. Unlike bar stock, plate stock is known for its broad, flat, and uniform surface, making it ideal for parts that need structural support. It is commonly employed in machining, construction, automotive, and metal sheet fabrication industries.
Plate Stock: Understanding the Manufacturing Process
The production of plate stock involves a series of steps that transform raw materials into flat, durable metal sheets. Discussed below is a quick breakdown of how plate stocks are usually manufactured.
-
Casting
During casting, liquid metal, in melted form, is put into molds. They are then cooled to make solid blocks. These blocks are often called “ingots” in professional terms.
-
Heated Rolling
After cooling, the solid blocks are heated while passing through heavy rollers. This helps reduce the thickness of metal sheets to meet the requirements and make wide, flat sheets.
Some manufacturers also like to employ cold rolling after heated rolling to ensure the durability of the blocks.
-
Sizing to Fit Requirements
Metal sheets are cut into different shapes and sizes by employing tools like water jets, laser machines, etc.
-
Treating with Heat:
Plates are put through certain heat processes to improve physical properties. For example, hardness and durability.
-
Surface Finishing for Durability:
At last, plates often go through some finishing processes like galvanising, painting, and polishing. They help reduce scratches and wear and tear. Similarly, they help improve corrosion resistance.
Plate Stock: Common Types and Usage
Several types of metal plates are staples for different industries. Some common types are discussed below:
-
Mild-Steel Plates
They are among the most affordable and easily fabricated plates. They can be cut, welded, and shaped to build structural components.
-
Galvanized-Steel Plates
Galvanised plates are coated with a protective zinc layer that significantly improves their rust resistance. They are commonly used in the automotive industry.
-
Treaded Plates
These plates have raised patterns like treads on a surface to provide grip. Thus, it is mostly employed in industrial areas.
-
Black-Iron and Galvanised-Iron Plates
B.I. and G.I. plates are heavily used in the construction industry. However, black iron plates are used indoors, while galvanized iron plates are used outdoors due to their zinc coating.
Bar Stock Vs Plate Stock: What is The Difference?
Although bar stock and plate stock are both raw materials used in the manufacturing industry, they have distinct structural characteristics and industrial applications that make them different.
The following is a breakdown of the features that make them comparable.
Shape:
- Bar stock has a solid, yet uniform shape. It is found in all round, rectangular, or square structures.
- Plate stocks are, however, solid, flat sheets with a uniform thickness throughout.
Dimensions:
- Bar stocks have a fixed cross-sectional area with long lengths.
- Plate stocks have a wider surface area. They are found in varying sheet sizes.
Manufacturing Process:
- Bar stocks are produced by extrusion, rolling, and drawing techniques.
- Plate stocks are made by casting, hot and cold rolling, and cutting.
Machining applications:
- Bar stocks are ideal for turning, milling, and lathe work.
- Plate stocks are a preferred raw material for CNC machining and metal sheet cutting.
Cost:
- Bar stocks are often more affordable.
- Plate stocks are more expensive due to their larger dimensions.
Aluminium Bar Vs Plate Stock: Better Decision for CNC Machining
When choosing between bar and plate stock, there are several factors you need to consider before making a final decision:
1. Part Size and Shape
For parts having a consistent and uniform structure, bar stock is the ideal choice. For example, rods, pins, shafts, etc. However, if the part must have a larger surface area or irregular dimensions, plate stock is often the preferred choice.
2. Material Availability and Cost
When comparing per pound, bar stock is usually the more cost-effective choice. It is mass-produced with standardized dimensions. On the contrary, plate stock is more expensive due to its certain requirements.
3. Surface Finish and Grain Structure
Bar stock has a uniform grain structure, which helps improve strength and dimensional stability. However, plate stock has directional grains that help it withstand precision.
4. Cutting and Edge Quality
Bars often have cleaner and smoother edges. However, plates need further finishing to meet tight requirements.
Bar Vs Plate Stock: Industrial Applications
Both bar and plate stock have important roles in the manufacturing industry, but their applications vary depending on different structural and industrial characteristics.
Aerospace
Bar stock is normally used to make lightweight, yet durable and efficient aircraft components. For example, actuator rods, support struts, landing gear, and hydraulic system shafts.
Automotive
Both bar stock and plate stock are used to manufacture engine-related components. It builds parts that provide structural stability, integrity, and support.
Construction
When used to build construction parts, bar and plate stocks provide durability, strength, and structural support; they ensure structural integrity when employed to support columns. This is enabled by their capability to resist external forces.
Premium Parts – Our Expertise
At Premium Parts, we promise to deliver high-quality precision-machined parts using both bar and plate stocks. From standardised sizes to custom-built shapes, we can tailor each part to fit your custom requirements. This helps ensure consistency, performance, and durability in the long term.
Whether you are working with stainless steel, galvanised iron, or plastic, our machining capabilities can help you serve a variety of industries. This includes aerospace, automotive, and industrial manufacturing.
Reach out to us, and let us bring your vision to reality.
Conclusion
Bar stock and plate stock are both foundational materials in modern manufacturing. Each comes with its essential characteristics and limitations side by side. Bar stock is ideal for parts having uniform cross-sections, while plate stocks are preferred in larger and flatter components.
Understanding the distinction between shapes, processing methods, materials, and practical applications can help you make the right decision. This is particularly useful for precision manufacturing.
At Premium Parts, we are here to support you at every step. Join hands with us, and let us help you achieve your project requirements with our high-end machining capabilities.
FAQs
Q1: Will it Help Me Save Money by Switching from Bar Stock to Plate Stock?
Usually, it can help, but this isn’t guaranteed. Bar stock is usually cheaper per pound, but plate stock is more economical by saving machining time for larger flat sheets.
Q2: Is Aluminium Bar Stock Stronger than Aluminium Plate Stock?
Strength depends on the grade and grain structure of the material employed. Bar stock usually has uniform grains; however, plate stock can be stronger if machined correctly.
Q3: Can I Customise a Bar Stock to Fit My Required Dimensions?
Yes, bar stock is custom-built by using operations like cutting, welding, and heat treatments. Therefore, they can be individually tailored to fit your dimensional requirements.