Choosing the right manufacturing process can either make or mar your project. Being an engineer, working on a new product for your customer. You may need to test various prototypes before advancing to or commencing mass production. Do you choose injection molding due to its durability and precision, or do you opt for urethane casting, which offers flexibility and speed? It all comes down to your budget, time duration, and volume requirements.
Generally speaking, if you are required to produce several 1000 parts, injection molding is a go-to option. Molding is built for high-scale manufacturing and cost-effective benefits at a large scale. However, if your production requirement is a few 100s, or you want to test a few prototypes, then urethane casting is an optimal option.
Overall, both techniques have their strengths in their operations. A keen understanding of these strengths and limitations will help you make the right selection for the desired output. Let’s break it down:
What Is Injection Molding?
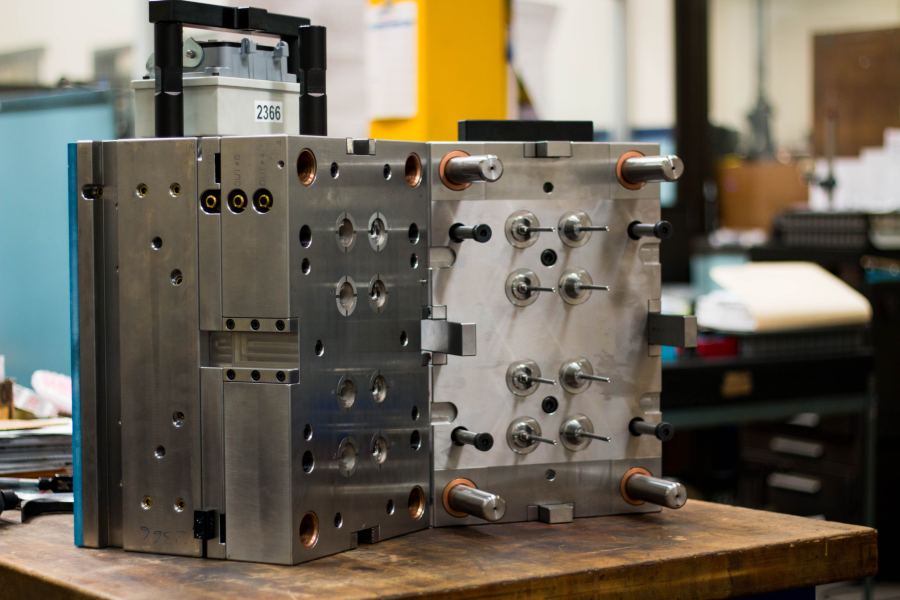
Plastic Injection Mold
Image Description: A close-up image of a plastic injection mold, showing its clean surface and detailed design used to shape plastic parts.
Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process typically used to produce high-volume, precision parts. It injects molten material, usually thermoplastic polymers, into a highly engineered mold under high pressure.
Professionals prefer this option in industries such as automotive, electronics, and consumer goods, where it is possible to create thousands of identical parts. Moreover, it is also efficient and precise, and can create intricate geometries, which makes it ideal for mass production.
Operation Breakdown
The molding process begins by creating a mold, typically made from steel or aluminum. Features such as cavities and channels for material flow are built into the mold, ensuring it is designed to match the final part’s shape. Thermoplastic material is heated to the point of melting and forced into the mold under high pressure once the mold is ready. The material is then melted, cooled, and solidified inside the mold. The mold is then cooled, and the part is ejected from the mold when opened.
Materials Used
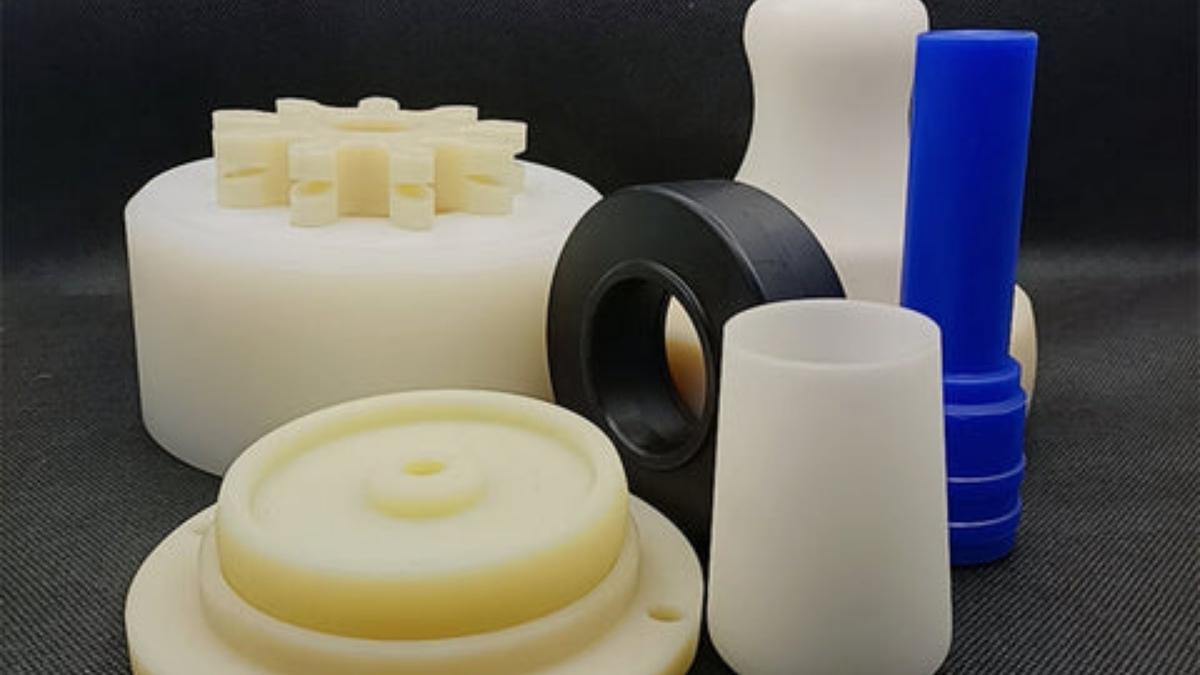

Nylon Injection Molding
Image Description: Custom nylon injection molded products, each with a unique shape and vibrant surface finish.
ABS, Polycarbonate, Nylon, and Polypropylene are fundamental thermoplastics used in the injection molding process. These materials are durable, heat-resistant, and high-performance, and are used in a wide range of applications. Generally, the part’s intended function and environmental exposure determine the material.
Key Advantages
- High production efficiency
- With tooling in place, it becomes feasible to produce parts in fast succession, thus reducing per-unit costs in large volumes.
- Injection molding also provides good precision and repeatability for complex geometries and intricate details.
Limitations
- Creating molds from metal is expensive, as it involves a high initial investment due to the high tooling costs.
- The process takes longer lead times, sometimes from weeks to months, to set the molds.
- For small-batch production or prototypes, injection molding is not economical due to high setup costs.
What Is Urethane Casting?
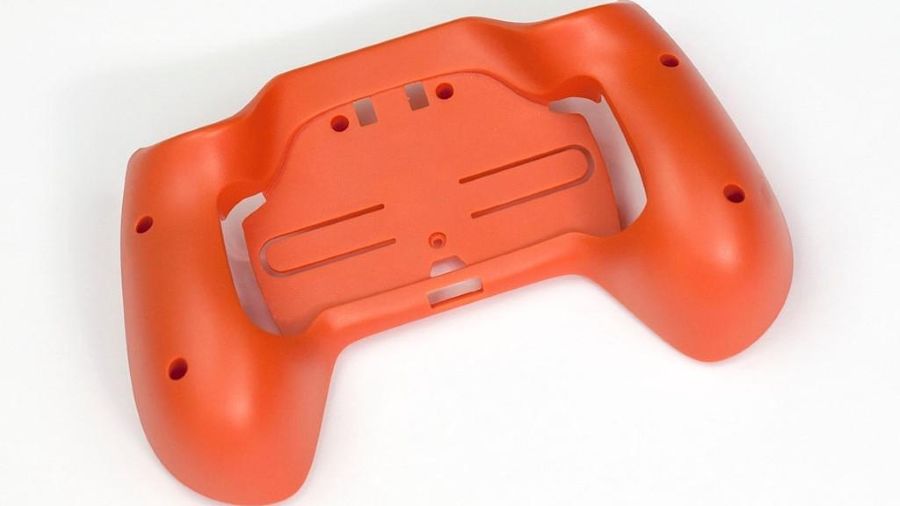

Urethane Casting
Image Description: An orange urethane-cast part, shown in detail with smooth surfaces.
Urethane Casting is a low-volume production and prototyping process used for low volume production. Unlike injection molding, the parts are made from a silicone mold, which is created from a master pattern. Since it is cheaper and faster, it is a better process for smaller production runs or when quick iterations are required. Designers use them in parts that require flexibility or special mechanical properties, which cannot easily be met with thermoplastics.
Operation Breakdown
The process begins with the creation of the master pattern (the prototype or model that represents the final part). A silicone mold is made from this master pattern. After the mold is ready, polyurethane resin is poured into it. The resin is then cured to become the desired shape. When the part is cured, it is removed from the mold, and the process is completed.
Materials Used
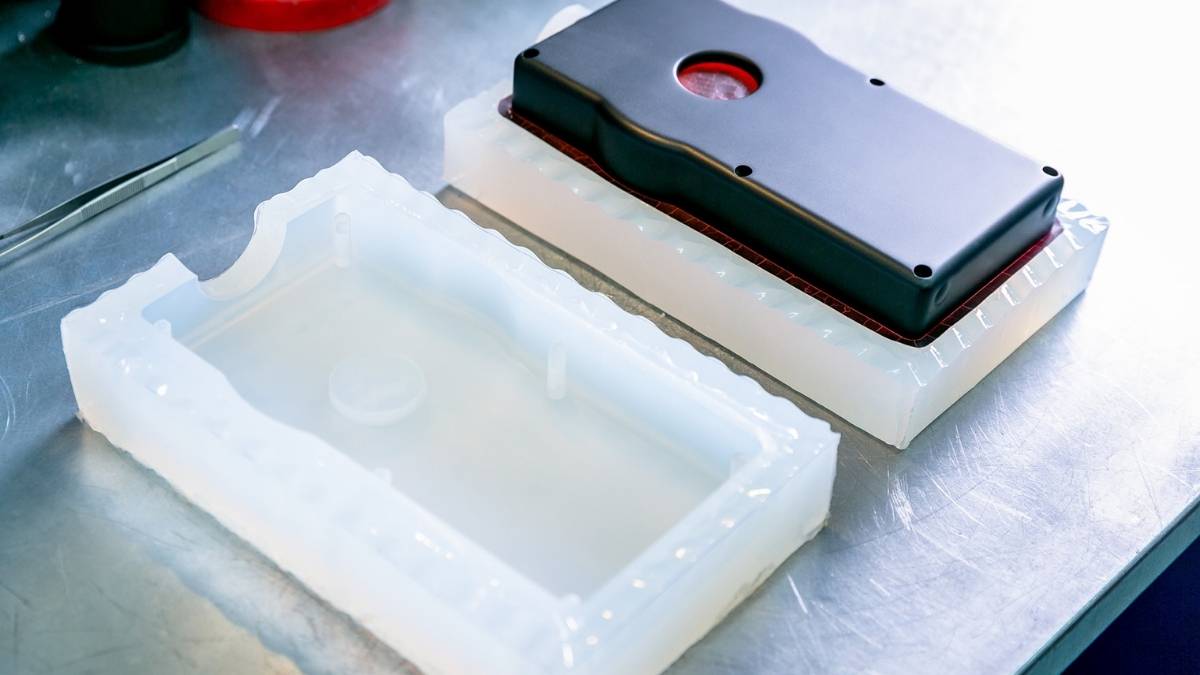

Polyurethane Casting
Image Description: A close-up of a polyurethane casting part being removed from the mold.
Urethane Casting uses common polyurethane resins. They can duplicate the properties of various thermoplastics and are flexible enough to make parts with desired qualities, such as flexibility or rigidity, in the formulation.
Key Advantages
- Urethane Casting is one of the cheapest methods of production for low-volume production.
- Since silicone molds are relatively inexpensive to produce, the initial tooling cost is significantly lower than that of injection molding.
- Urethane Casting is ideal for prototypes or small-batch parts where high volume is not required. The process is also faster than injection molding, making it an ideal choice when speed is critical.
Limitations
- Due to the shorter lifespan of silicone molds, which typically last only 20–25 uses, they are not ideal for large-scale production.
- Urethane cast parts are not as precise as injection molding
- Parts requiring tight tolerances are not as suitable as urethane-cast parts.
Injection Molding Vs. Urethane Casting: A Detailed Comparison:
Are you unsure whether to choose between injection molding and urethane casting? You can consider cost, turnaround, material properties, and production volume. Let’s compare each process in detail.
Table 1: Injection Molding Vs Urethane Casting: Comparison Summary
| Feature | Injection Molding | Urethane Casting |
| Initial VS Per unit cost | High capital due to metal molds | Low initial amount, because of silicon-based mold |
| Speed & Production Time | Mold making takes several weeks to months | Molds ready in 5-10 days |
| Material Properties & Durability | High durable. Suitable for thermoplastics like ABS, Polycarbonate, and Nylon | Less durable. Uses thermoset polyurethanes. |
| Surface Finish & Accuracy | High tolerance within ± 0.05 mm | Comparatively less tolerance values i.e., ±0.1-0.3 mm |
| Production Volume | Ideal for mass production of (10000+ units) | Ideal for less volume items (Several hundred) |
| Design Flexibility & Materials | Limited flexibility and machining/repairing are costly and time-consuming. | Highly flexible, best for prototyping. |
Initial vs. Per Unit Cost Analysis
Since injection molding employs metal molds, it incurs higher expenses. However, it becomes economical in high-volume production (usually above 10,000 units). Once the tooling is established, the per-unit cost drops dramatically. Urethane Casting uses silicone molds, which are cheaper to make, and hence, tooling costs are lower. Nevertheless, the per-unit cost for urethane casting is more expensive than injection molding and is suitable for low-volume production (10–500 units).
Speed & Production Time
Tooling setup in injection molding takes 4–12 weeks. The cycle time for each part is 30 to 60 seconds, after which it is efficient for large production runs. If the need is for faster prototypes, urethane casting can offer molds in 5-10 days, and the casting cycle time is 30 to 60 minutes per part. Additionally, urethane casting offers a faster lead time and is suitable for prototyping and small production runs.
Material Properties & Durability
Injection molding utilizes thermoplastic materials, such as ABS, Polycarbonate, and nylon, to create unique design features. These materials provide high strength, durability, heat resistance, and chemical resistance. On the other hand, urethane casting utilizes polyurethane resins. They are not as durable and possess lower heat resistance than injection-molded parts.
Surface Finish & Accuracy
Injection molding provides high precision with tolerances as tight as ±0.05 mm, offering consistent, high-quality finishes across large runs. On the other hand, the surface finish is also consistent, available in glossy, matte, or textured finishes. However, Urethane Casting is less accurate (±0.1–0.3 mm) and may require further post-processing, such as sanding or coating, to achieve a better finish. Since the cosmetic finish is not the priority, it is better suited for low-tolerance parts or prototypes.
Production Volume: Small vs. Large Runs
For large-volume production (10,000+ parts), injection molding is best when the lower per-unit cost at scale offsets the initial tooling costs. In contrast, urethane casting is a suitable choice for low-volume production (10–500 parts), particularly for rapid prototyping, small batch runs, or when minimizing tooling costs is necessary.
Design Flexibility & Modifications
The ease and low cost of changing silicone molds make urethane casting a more flexible design option. It is a preferred choice for iterative design or prototyping. In contrast to injection molding, it is less adaptable to design changes after tooling is complete due to the high cost and time required to make mold modifications.
Tooling & Mold Life
Metal molds are used in injection molding, which has a lifespan of 100,000+ cycles or more for high-volume production. Silicone molds are used in urethane casting and generally last 20–25 cycles, which makes them more suitable for short-term, low-volume applications.
Whether you are testing designs or scaling up your production, our professionals at PremiumParts can provide tailored solutions to scale up your production. Contact us today!
Real World Case Studies
Urethane casting for GoPro Outer Body
For its iterations of different camera series, GoPro, one of the top action camera manufacturing companies, used a polyurethane casting procedure.
Why Urethane Casting?
- It helped in iterating various complex designs with no high-cost tooling requirements.
- Within a week, the silicone molds were ready for prototyping, which helped speed up the process.
- Improved final item properties by the utilization of polyurethane resins.
Outcome:
GoPro was able to iterate its camera designs within weeks through urethane casting, minimizing time to market by a large margin.
Injection Molding for LEGO Bricks
LEGO is one of the iconic toy manufacturing companies. It heavily relies on injection molding technology for the production of billions of plastic bricks per annum.
Why Injection Molding?
- It helps achieve high tolerance values for highly precise plastic brick-making.
- Large production with precise dimensions and quality.
- Used ABS-based plastics for precision and durability.
Outcome:
LEGO confirms scalability and durability by using injection molding to make more than 3600 bricks per minute with desired dimensions.
Key Reasons for Selecting the Best Manufacturing Option:
Here are the best tips for selecting the right manufacturing technique:
What are the Material Options?
If you are designing for functional parts that will be exposed to harsh conditions, such as automotive components and electronic housings, you should opt for injection molding. It allows you to use high-performance materials, such as ABS or Nylon, that resist heat, chemicals, and physical stress. However, if your project involves prototyping or small-volume parts that will not be under much stress, urethane casting may be a better choice. For non-functional parts, where flexibility is more important than extreme durability, it is the dominant factor.
What Lead Time and Setup are needed?
Injection molding is beneficial for large-scale production. Once the tooling has been paid for, the per-unit cost is minimal, making it a wise choice for mass production. However, if your project involves low-volume runs or rapid prototyping, such as creating a prototype for testing, then Urethane Casting could be more beneficial. The upfront cost is low, which helps you test your designs without a hefty investment.
What are the Expected Production Volume and Cost Efficiency
Urethane Casting is ideal when time is critical, such as when you need a prototype in a matter of days to meet a project deadline. In a few days, you can be ready with your molds. Injection molding is better suited for long-term, high-volume production runs, especially when time is not a constraint.
How Much Modification Do You Need in Your Mold?
Urethane Casting, however, is more flexible if your project involves numerous design iterations or if changes are expected to be frequent. For instance, if you are developing a new product and require to modify your prototype multiple times before finishing, this method is far less expensive and easier to change. Injection molding will be more efficient once the tooling is set, but less adaptable during the design phase if you’re working on a finalized design for mass production.
Summary
By understanding the differences between injection molding vs urethane casting, manufacturers can optimize production costs, increase efficiency, and meet certain project requirements. Large-scale production typically requires injection molding, which is precise, durable, and offers lower per-unit costs at high volumes. However, Urethane Casting is more suitable for small-batch production and prototype needs, offering faster turnaround and greater flexibility. Both procedures have their benefits. Selecting the right one depends on your manufacturing requirements, including material selection, cost, lead time, and production scale.
Order High-Quality End-User Products From Premium Parts
At Premium Parts, we offer high-quality molded parts tailored to customer requirements. Whether you need prototypes for rapid development or precision-molded components, we offer seamless production solutions. Our advanced techniques ensure durability, accuracy, and cost efficiency, regardless of the production scale. From automotive to consumer products, we help our customers deliver flawless and precise items. If you are looking for high-performance and customized molded parts? Contact us to get manufacturing excellence.
FAQ’s
Q1: Which process is more cost-effective?
Urethane Casting is good for low-volume, low-cost prototyping. At the same time, injection Molding is good for high-volume production.
Q2: Which procedure can make the product quickest?
Urethane Casting has a quick turnaround. Conversely, injection molding has a longer setup time but runs faster in mass production.
Q3: Which process gives more material strength?
High-strength thermoplastics enable the production of durable and high-performance parts through the injection molding process.
Q4: Which process should I choose for prototypes?
For functional prototypes, Urethane Casting is the best option due to its low tooling costs and quick production.