CNC Rapid Prototyping
CNC Rapid Prototyping
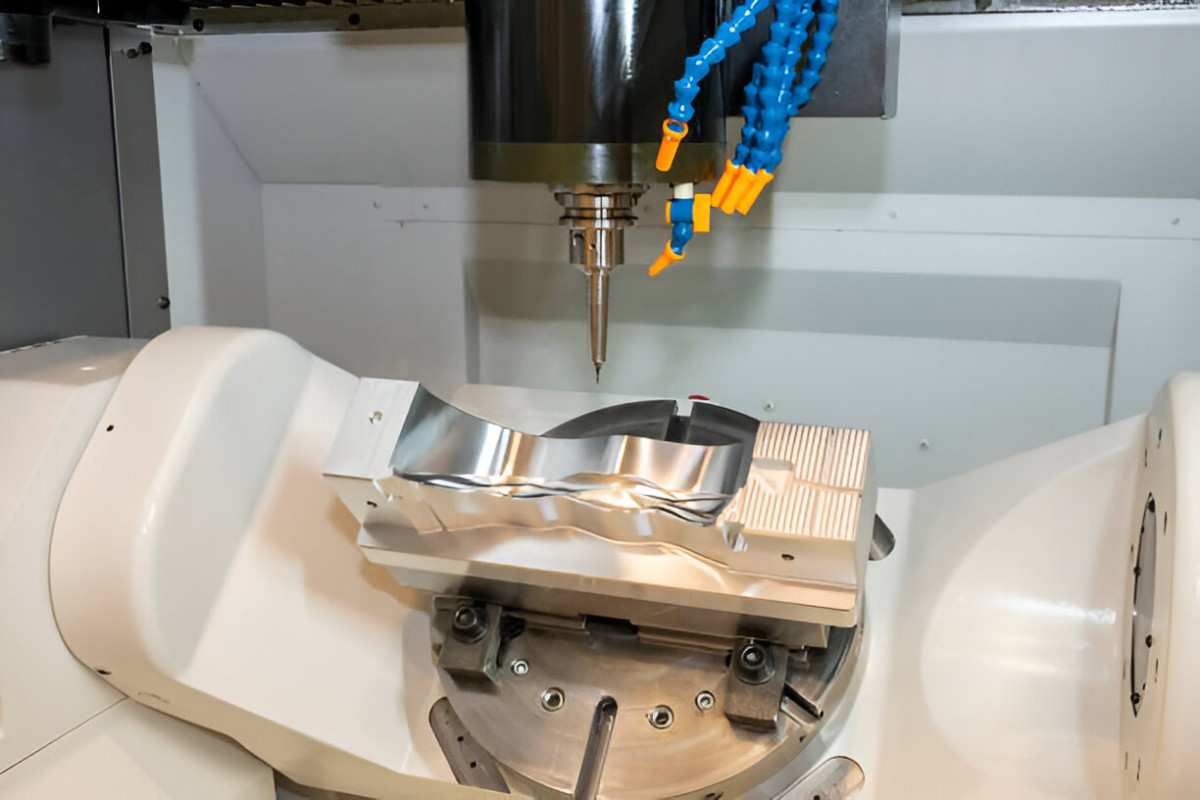
Image Description: A CNC machine is machining a metal part for rapid prototyping. The workpiece is clamped while the cutting tool shapes it precisely.
Rapid prototyping is a manufacturing process that employs specialized production techniques to create high-fidelity physical prototypes. Designers generally use prototypes for evaluating design, testing functionality, controlling quality, iterating concepts, and improving the design. By delivering quick and economic models, prototypes provide valuable insights into a product concept. And they can be critically evaluated before mass production proceeds. What’s more, rapid prototyping is extremely fast because the process doesn’t require hard tooling.
CNC Machining is one of the most effective means for rapid prototyping. The process allows you to take advantage of the CNC to deliver high-quality prototypes in a quick turnaround period. Here are more reasons why CNC machining should be your preferred technique for making rapid prototypes.
1. Speed
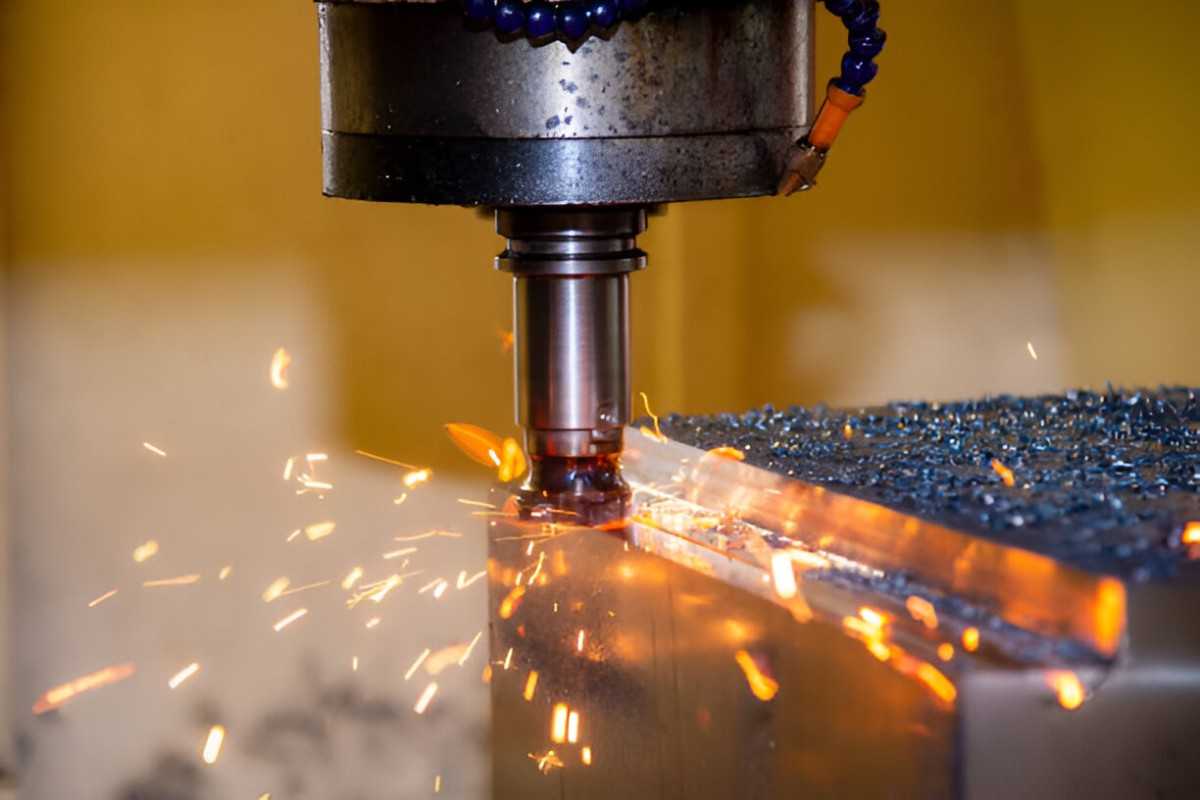 High Speed Machining
High Speed Machining
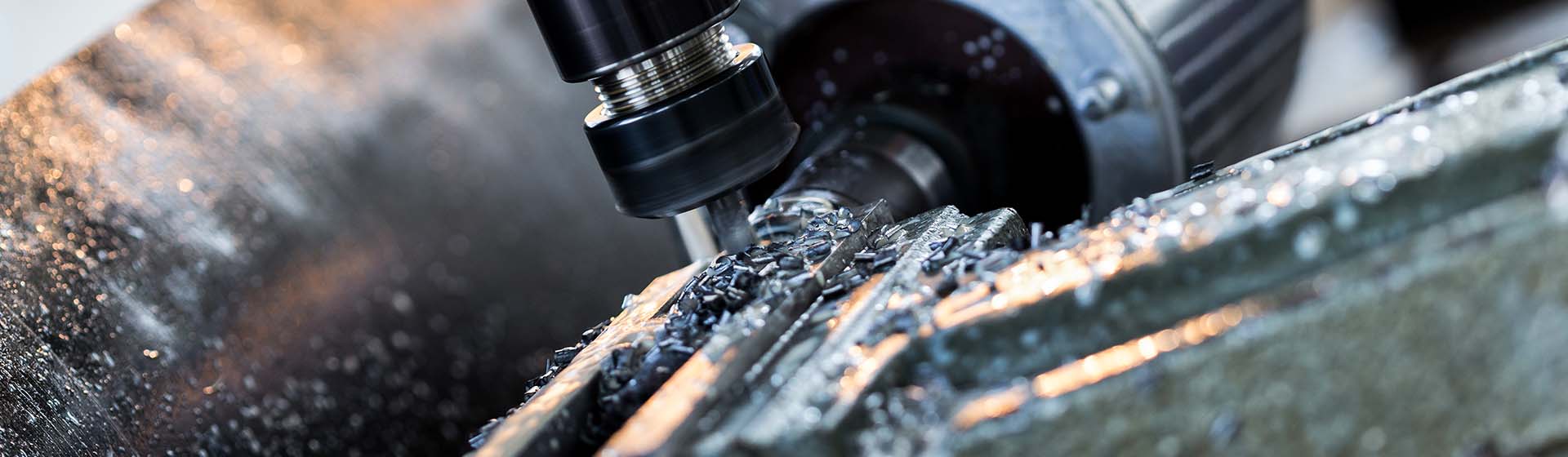
Image Description: High-speed machining in progress with visible sparks flying from the cutting area.
CNC Machines have greatly improved since their inception in the 1970s. The additional axes controls have greatly accelerated the capacity of CNC machines to deliver higher quality at improved speeds.
As rapid prototyping demands genuine models with fast turnaround times, CNC machining is considered one of the preferred methods in the industry for obvious reasons. From setup times to actual execution, CNC machines will translate 3D CAD/CAM models into G-code software and then commence milling to produce the final part in several hours.
CNC milling techniques offer almost zero downtime during the production process. These can operate continuously and allow lights-out manufacturing, where machines function unattended during off-hours. Their capability increases productivity, especially when used in prototyping, where time is critical. Manufacturers can make several prototypes at the same time or one after another. This speeds up development because they don’t need constant monitoring.
Moreover, CNC technology brings quick adjustments to the machining process when needed. Design changes are common in prototype making, and you can easily implement these alterations using CAD software. The new design can be re-adjusted to produce a new G-code with little or no intervention. So, this lets you recalibrate machining parameters instantly.
This flexibility is ideal for prototyping since it often means trying different ideas to find the best solution. Such services also include simulated CNC tools that allow engineers to model and check tool paths before implementation to mitigate mistakes and achieve the best machining processes.
Overall, the combination of automation, continuous operation, and flexible programming capabilities of CNC machining makes it appropriate to offer high speed and efficiency in the fabrication of rapid prototypes. The advantages of fast reaction to design changes and the flexible organization of the production processes not only increase efficiency but also guarantee the standard quality of prototypes.
2. Tooling
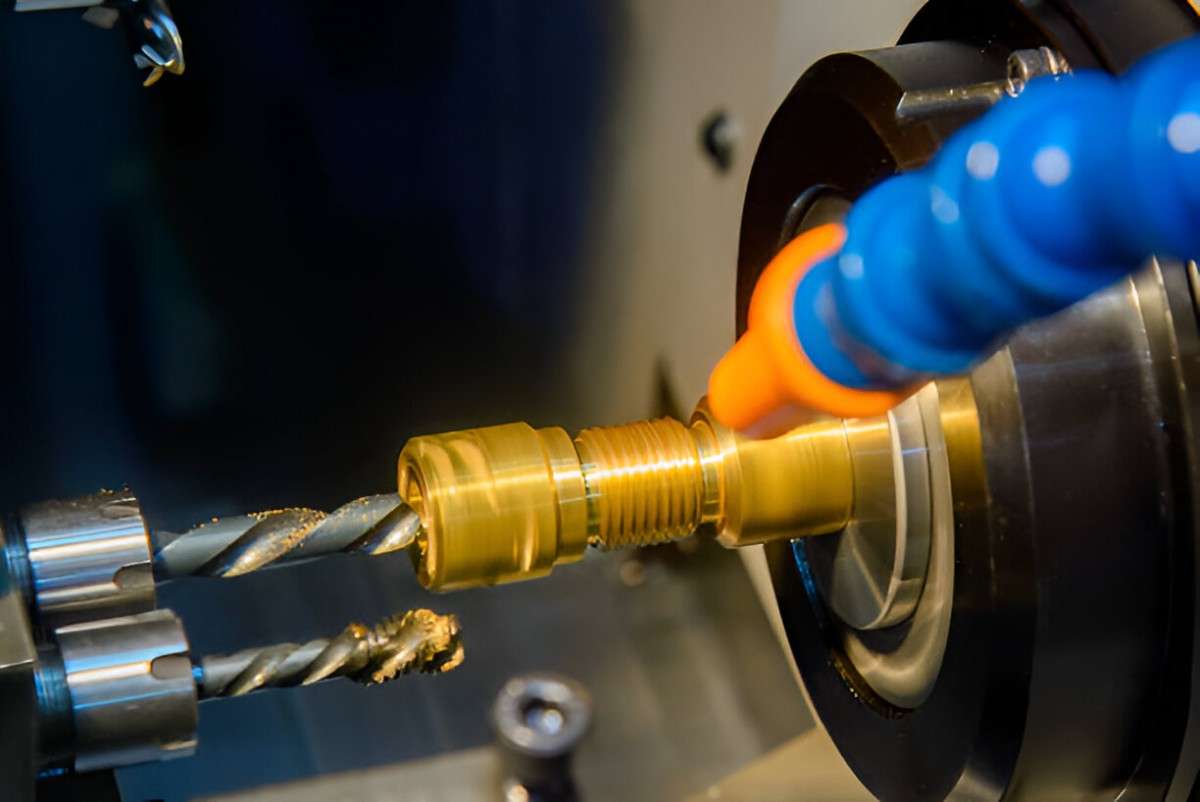 CNC Tooling
CNC Tooling
Image Description: A Swiss turning machine in operation. It shows the precise machining process with a visible tooling setup.
For manufacturing techniques like pressure die casting and injection molding, there is usually a need for a rigid die from steel alloys. This raises the cost of processes. These dies can take weeks to manufacture based on design complexity and the desired shape. Additionally, the errors in the details of these dies will automatically be reflected in their copies.
CNC machining, on the other hand, requires no fixed tooling. The process only requires a CAD/CAM design, software integration, and some sort of cutting tools to execute production. Because of this, it is considerably faster, cost-efficient, and more accurate for rapid prototype manufacturing. However, tools may be required for production in large batches. So, it’s crucial to understand their significance and workability.
2.1. What Makes Tooling Essential?
- Precision Engineering: Tooling is always curated based on specific designs and standards. It allows CNC machines to produce parts with high precision. Accuracy comes from precise tooling. This ensures prototypes match the near-designs of products, especially in aerospace, automotive, and medical, where accuracy is central, and parts need to be precise.
- Adaptability: You can equip CNC machines with various tools to work on different materials and shapes. This adaptability makes it possible for manufacturers to quickly change between projects. For example, having multiple end mills for milling or different drills can perform many designs without significant tool changeover.
- Efficiency in Production: The right choice of tooling results in the best possible machining conditions, including cutting speed and feed rates. Optimization is identical for cutting cycle times faster, especially when using techniques such as rapid prototyping, where time to market is a factor. Tooling systems have automatic tool changers. This makes switching tools easy.
- Material-Specific Tooling: It’s important to recognize that the outcome depends heavily on the material and tools used. For instance, to machine aluminum may need a different tool than machining titanium. The specificity makes the tool run effectively, extends the tool life, and also retains the surface finish quality.
- Quality of Prototypes: Tooling is key to achieving high surface quality and overall quality in the final product. In the case of rapid prototyping, where the objective at many times is to build fully functional models for testing, achieving a good finish and accurate dimensions is crucial for confirming design and functionality.
2.2. Types of Tools Used In CNC Machines to Produce Quality Prototypes
CNC machining tools are usually manufactured from a combination of materials. Each material has the desired characteristics that can improve efficiency and tool longevity.
- High-speed steel is popular for its toughness and durability. Design manufacturers commonly use it for drill bits and end mills. It handles high speeds well and works effectively on materials like steel and aluminum.
- Carbide tools possess high wear resistance, high heat conductivity, and are thermally stable. They are heatproof and can last for a long time. These tools are suitable for use on materials such as stainless steel and titanium. They can be used in tough conditions.
- Cobalt alloy in high-speed steel improves the heat material treatment properties. This material is perfect for roughing due to its machining strength. It incorporates the properties of strength with heat resistance. This makes it suitable for use on difficult-to-cut materials.
- Ceramic tools are very hard and best suited for use with brittle material. They are good on cast iron and are capable of withstanding high temperatures. Nevertheless, ceramics are very fragile materials and therefore not suitable for use in most applications.
- PCD tools are extremely hard. So they are ideal for cutting non-ferrous materials such as aluminum and any composite materials. These tools are especially helpful when manufacturers produce a large number of similar products.
- Cermet tools consist of the desirable properties of ceramics and metals. These materials provide good wear resistance and a high level of toughness for finishing operations. These tools are useful in hard steels and nonferrous materials. They contribute to improving the total CNC machining performance flexibly.
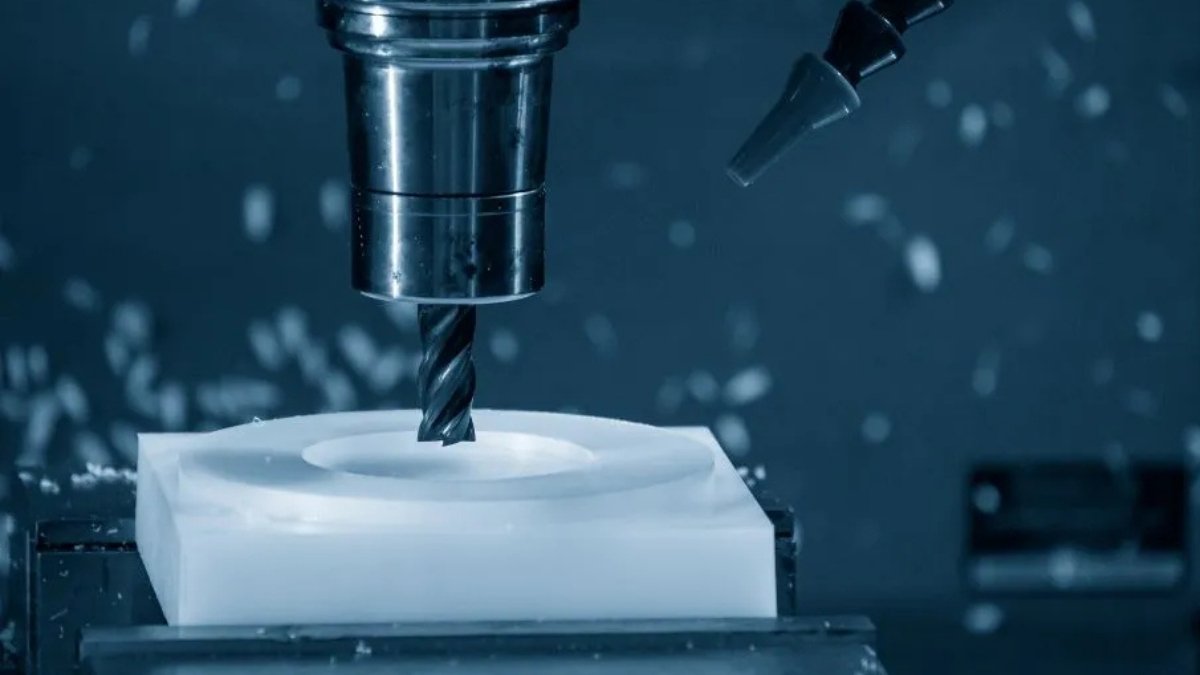
3. Accuracy and Precision
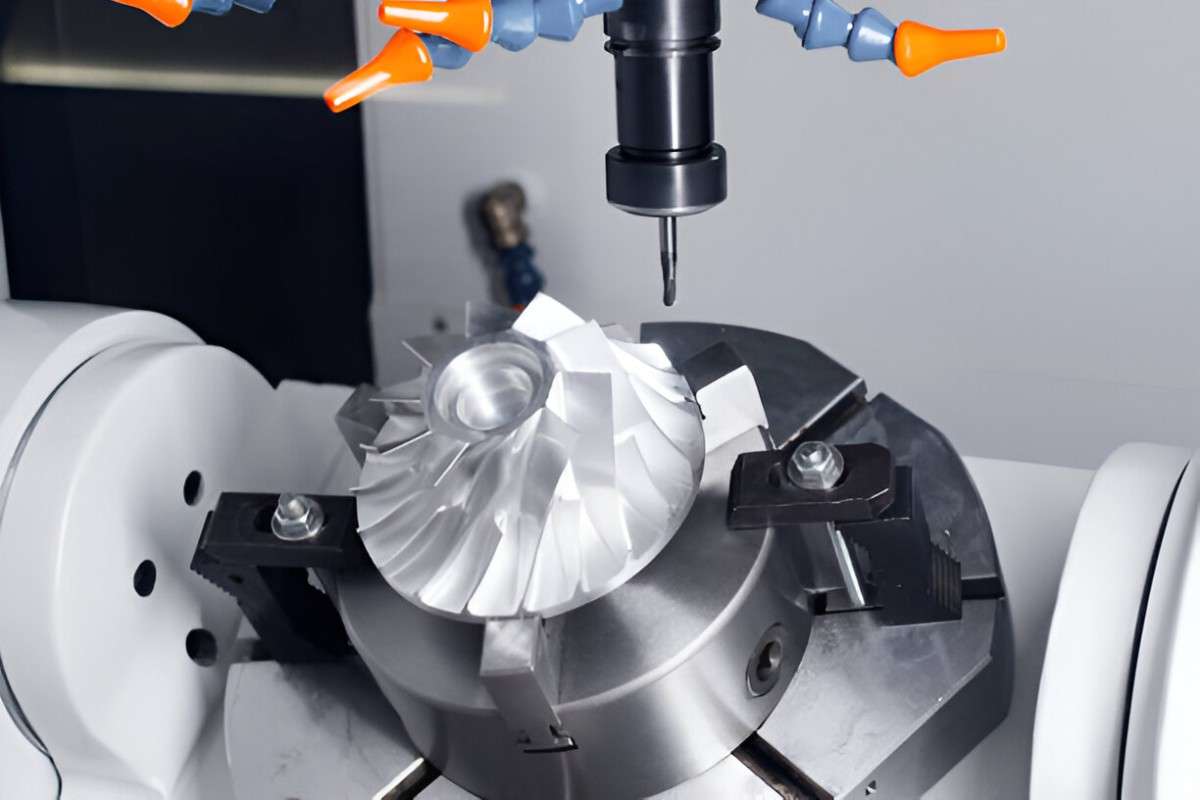 Precision CNC Machining
Precision CNC Machining
Image Description: A CNC machine is making a detailed precision part with exact dimensions.
No other manufacturing process in the industry can match the accuracy and precision offered by CNC machines. In modern production hubs, the CNC is the most effective way of achieving the highest level of accuracy with tolerances in the neighborhood of 0.05mm, give or take.
CNC machines also offer highly scalable and repeatable accuracy. So, helps ensure all produced prototypes look and function almost identically. The tolerances achievable with CNC machines are so precise that they are suitable for nearly all commercial applications in which they might be used. Here are the common CNC operations employed to create functional prototypes.
CNC Milling
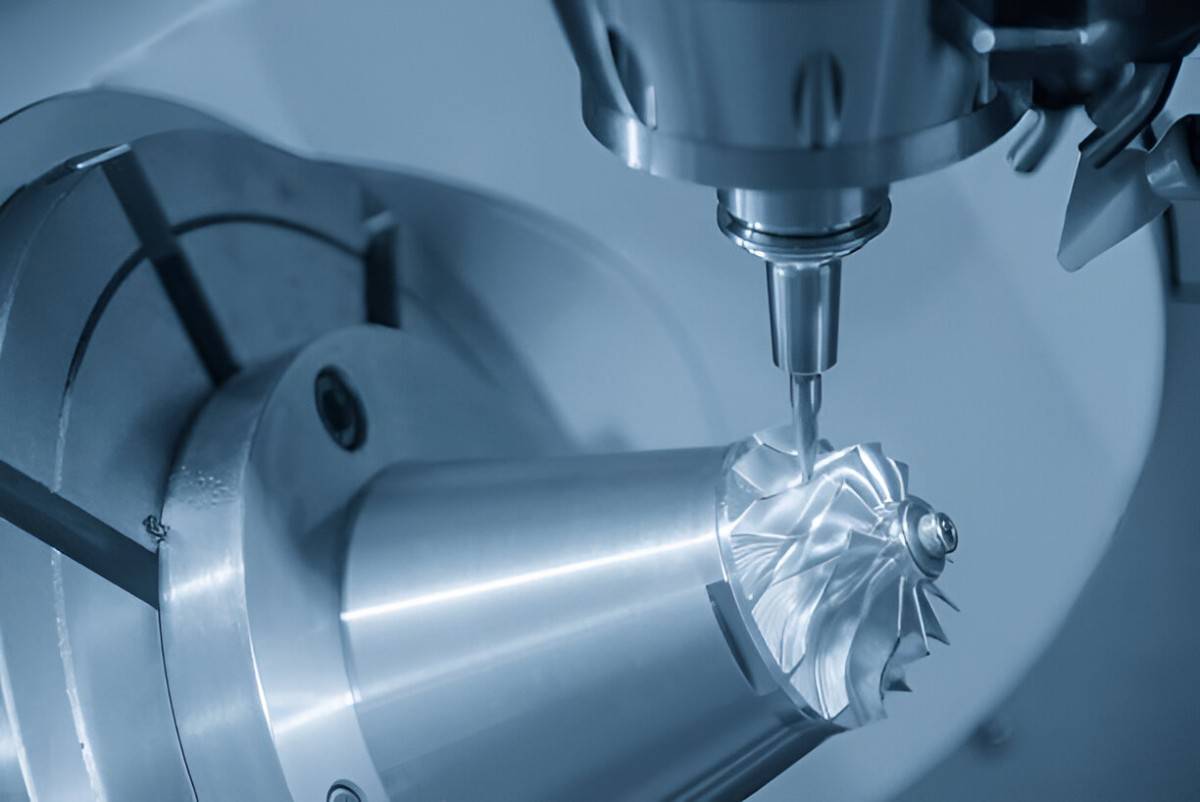 CNC Milling Prototype Machining
CNC Milling Prototype Machining
Image Description: The image depicts a CNC milling machine making a prototype part.
CNC Milling is a prominent precision technique in manufacturing. It can deliver tolerances of ±0.0005 inches and ±0.0127 mm with high-quality tools and proper setup. The process employs tools typically mounted on spindles. These tools move in different axes to cut material from a stationary workpiece, to create formidable shapes and features.
CNC Milling is widely adopted in the aerospace and automotive, and electronic sectors. These sectors require precise machining components for improving fuel efficiency and parts longevity. Furthermore, it can also deliver uniform or evenly finished, with Ra values of 32µin or better, while necessary for parts that have to be functional and cosmetic in equal measures.
CNC Turning
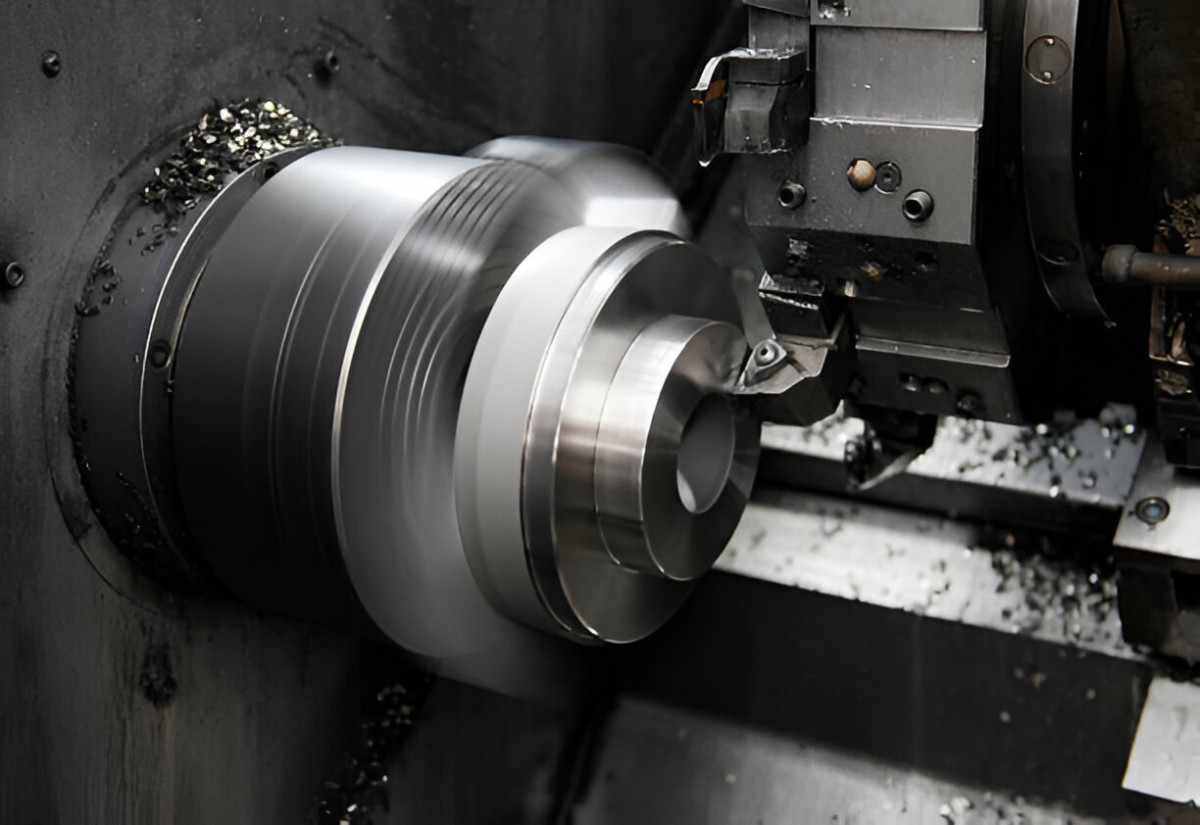 CNC Turning Operation
CNC Turning Operation
Image Description: A close-up of a CNC turning operation on a part.
CNC turning also stands as one of the most vital processes to create complex parts with symmetrical features. The process usually produces a dimensional accuracy of ± 0.0002 inches (± 0.005 mm). In CNC turning, the workpiece turns around an axis while a cutting tool is held still and interacts with the material. This approach leads to small surface roughness and equal cross-sectional area, meaning that dimensional variation is reduced. The process is effective in delivering a high surface finish, often delivering Ra values of 16 µin or better, and is appropriate for high-tolerance components such as shafts, gears, and other rotary parts.
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
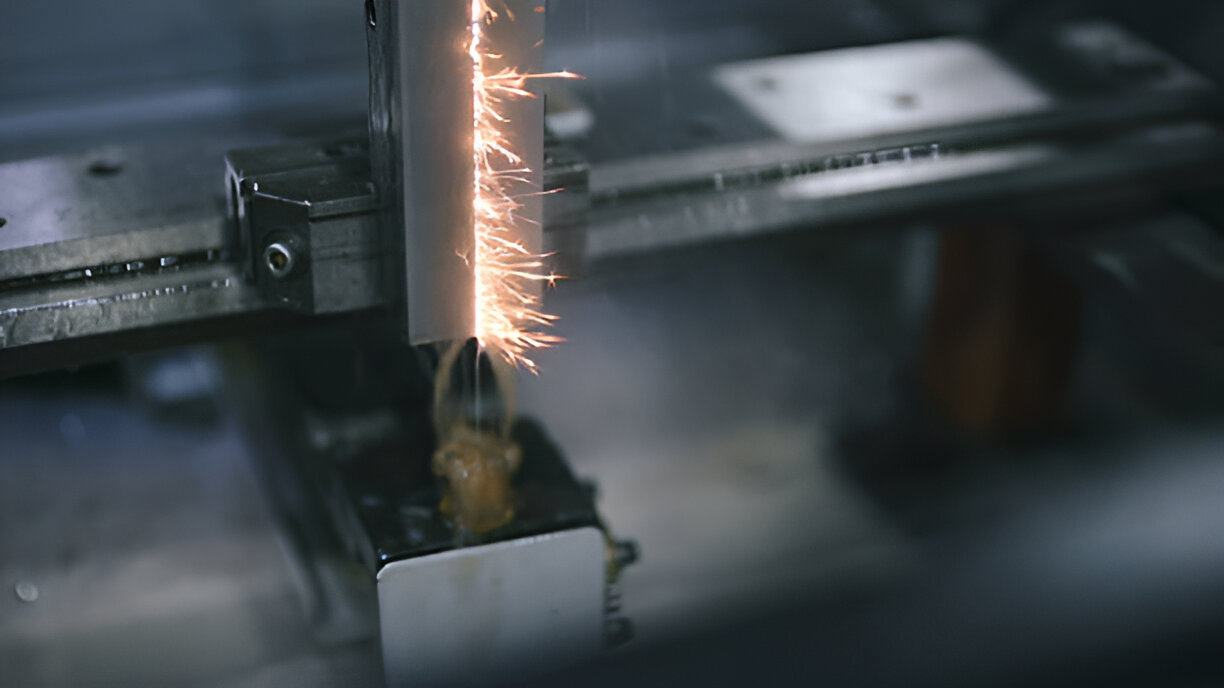 EDM Machining
EDM Machining
Image Description: A wire EDM machine cutting a part with visible sparks.
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) can be employed where higher accuracies are necessary. EDM can be accurate within ±0.001 inches (±0.025 mm), making it ideal for designing complicated shapes and difficult-to-cut materials. This process uses electric sparks to cut the material and allow for shape carving while avoiding mechanical stresses that are integral to most cutting processes.
The tight tolerance design provided by EDM is most beneficial to industries, for instance, in the aerospace and medical equipment industries, where components manufactured must meet certain performance specifications.
Verifying that the required tolerances are met determines the accuracy of CNC machining. There are different ways of determining the accuracy of a machined part through measurement. Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs) are used for making accurate three-dimensional measurements and are crucial to quality assurance in manufacturing industries.
Rapid and accurate surface measurements can be obtained from laser scanning technologies, while for in-process checks, conventional instruments such as gauges and calipers are used.
Most CNC systems come with some in-process measurement features that enable them to monitor the operations of the machine and make corrections should there be a deviation. Preliminary findings also indicated concerns regarding the possible future need for expensive recalibration of the CNC machinery to maintain the effectiveness of the processes in place.
Here’s a brief table that includes various technical aspects of several rapid prototyping machining methods:
| Rapid Prototyping Technology | Accuracy | Prototype Types | Applications | Technical Aspects |
| CNC Milling | ±0.0005 in (±0.0127 mm) | Complex shapes and features | Aerospace, automotive | Uses rotating cutting tools; can machine various materials; ideal for high-speed production. |
| CNC Turning | ±0.0002 in (±0.005 mm) | Symmetrical parts like shafts and gears | High-tolerance components | Workpiece rotates; suitable for cylindrical shapes; minimizes surface roughness. |
| Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) | ±0.001 in (±0.025 mm) | More complicated shapes | Aerospace, medical equipment | Uses electrical sparks to erode material; effective for hard materials; avoid mechanical stress. |
4. Control and Modifications
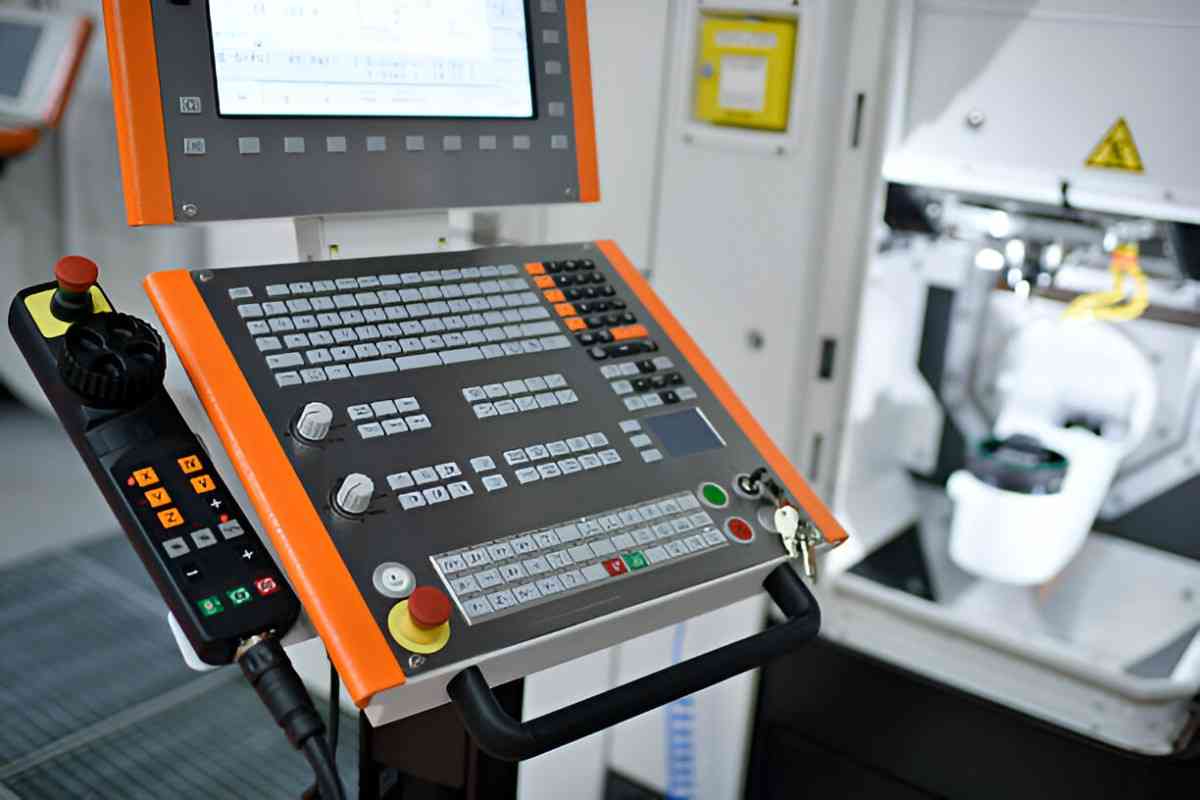 CNC Machining Control Panel
CNC Machining Control Panel
Image Description: A close-up of a CNC machine touch panel with controls and display.
Simply altering a few lines in the software program can modify an entire manufacturing process to match new specifications in just a few seconds. The G-code program enables highly interactive and controlled prototyping, allowing users to run multiple design iterations by merely refining and tweaking certain specifications without incurring additional costs. This is a great advantage over conventional manufacturing and prototyping techniques, where modifications may require new dies or expensive modifications to existing ones.
5. Material Variety
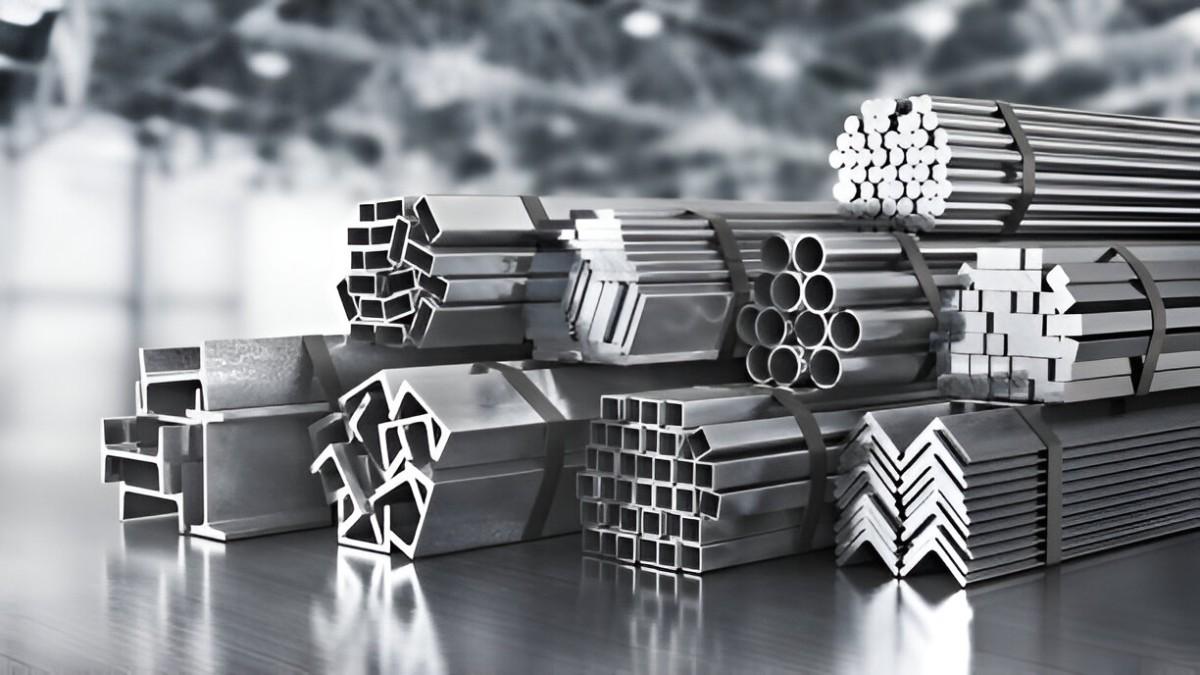 Metal Stock for CNC Machining
Metal Stock for CNC Machining
Image Description: Stacks of metal plates and bar stock prepared for CNC machining.
CNC machines are, for the most part, unselective machines. This means they will cut and mill various types of material for production. As long as the material is strong enough and does not deform under pressure.
CNC machining is suitable for rapid prototyping as it allows many developers to run multiple prototypes of their parts from various materials. This way, the same design can be made from several materials to evaluate the option with the best-fit mechanical, functional, and physical properties for its end use. With only small modifications to the feed parameters and running speed, the same design can be run across several materials to get the perfect prototype and ideal product.
You can use CNC machining effectively with various materials, allowing you to create different prototype parts. Here are some common materials and the prototype parts they often make:
- Aluminum(6061, 7075): Automotive parts, brackets, housings.
- Stainless Steel(304, 316, 17-4 PH): Medical devices, valves, and such structurally related parts.
- Plastics (e.g., ABS, Polycarbonate, Nylon): Covers for consumer products, model casings for electronics, and fittings.
- Titanium ( Ti-6Al-4V, Ti-5Al-2.5S): Lubrication parts for airplanes, body elements for medical equipment, and automotive components.
- Brass (C360, C377): Fittings, valves, and ornaments.
- Composites (e.g., Carbon Fiber, Fiberglass): Lightweight panels, structural parts, and aerospace mockups.
These materials enable versatility in application that makes CNC machining suitable for prototyping across many industries.
Premium Parts CNC Machining Services in China
Premium Parts is your go-to source for all CNC prototype needs. At Premium Part, we offer high-quality CNC machining services for different industries. Our expertise ranges across several services, and we can generate exceptional quality products with a quick turnaround. We can work with an extensive range of materials and produce both low and mass manufacturing volumes. Our highly experienced team will deliver best-in-class manufacturing quality and standards.