Boring Machining is a precision machining process. It is most commonly employed to enlarge the sizes of existing holes. Boring generally uses a rotating tool to shave off the intended material to expand the hole’s diameter. Normally, it is used on high-strength metals and plastics. The major purpose of boring is to hold close tolerances of size and shape and improve sthe urface finish.
The boring process entails rotating a metal around a hole as a cutting tool. After each cycle, the tool cuts the material from the inside of the workpiece, making it larger and more symmetrical. The engineers apply it when precision is valued significantly in the process. For instance, in engines and heavy machinery parts. Besides, boring has great control of the hole dimensions. It also guarantees that the holes are neat, accurately sized, and shaped to meet the needs of the required applications. It is used especially after drilling and casting to enhance the quality of the hole. The process offers the best finish with few iterations. Therefore, it is an essential method in the automotive industry, manufacturing, and aerospace engineering. For accurate measurements of holes, boring is the precise way of participating. Now, let’s look at boring machining from a more profound perspective.
What Is The Purpose of Boring Machining?
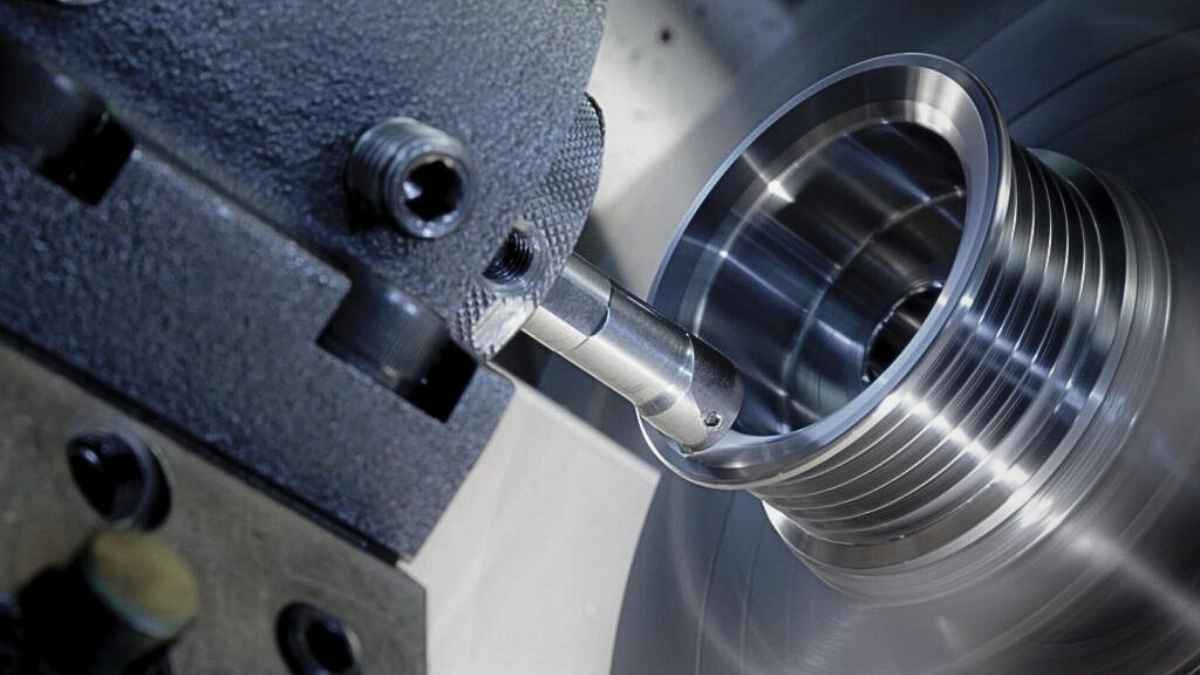

Boring Machining
Image Description: An image of boring machining in action. It showcases a cutting tool precisely enlarging a hole in a metal workpiece, with visible metal shavings around the machining area.
The core purpose of boring machining is to increase the hole’s diameter with accuracy in the required dimensions. While drilling makes the first hole, boring enhances the hole to reach certain sizes, lengths, and surface quality. Moreover, it ensures that holes are drilled to the required precision intolerance in different industries such as aerospace, automobile, and machinery industries where accuracy in the function of parts is paramount.
In addition, it maximizes the quality of holes produced by other means, such as drilling or casting, that may be used in combination with boring operations. Reducing the roughness of the surface and defective areas makes the component fit perfectly and perform optimally. Such a level of accuracy is particularly important when constructing components that must interface with other components to reduce failure rates in high-stress situations.
How Does Boring Machining Work?
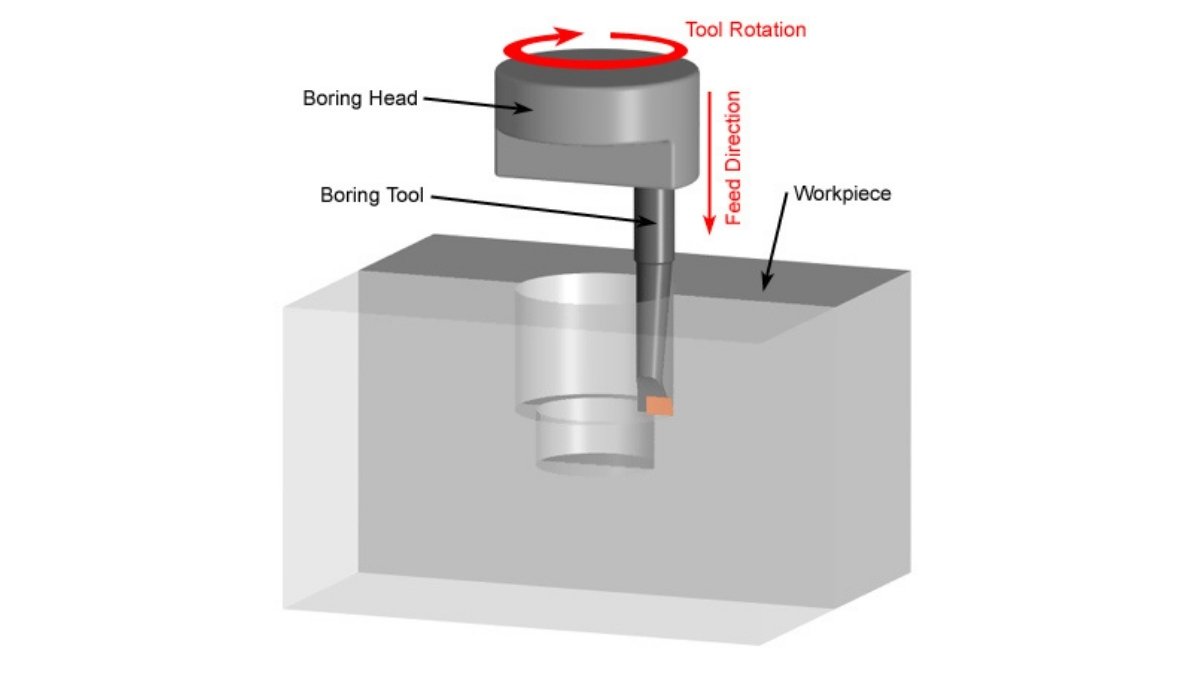
Boring Machining Process
Image Description: An illustration of the boring machining process. It visually displays how the cutting tool rotates inside a pre-drilled hole, gradually enlarging it to achieve precision.
The process of boring machining involves the following steps;
1. Setting Up the Machine
Boring machining starts by mounting the workpiece on the boring machine. For stability during the process, you must tightly clamp the part onto another part. Moreover, extra care needs to be taken into account to guarantee the right positioning of holes.
2. Selection of Tools and Tool Modification
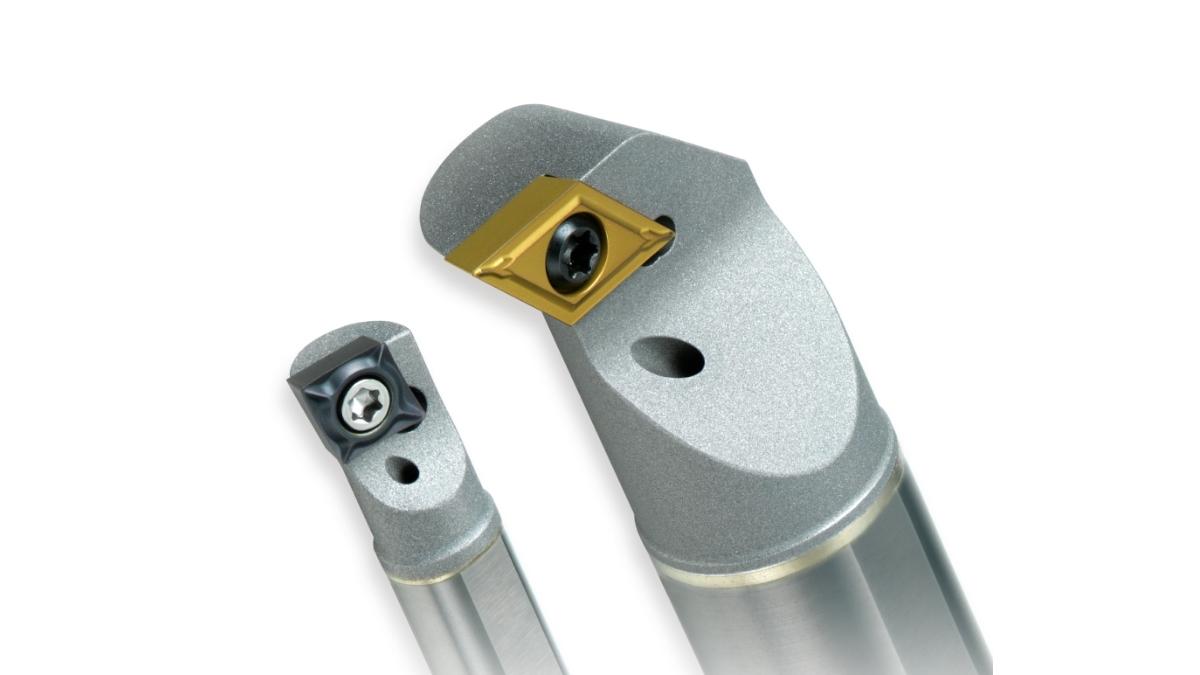

Boring Machining Bars For Tiny Parts
Image Description: A set of boring machining bars designed for tiny parts, showcasing their slim, precise cutting edges.
Then, the suitable cutting tool is selected. The tool is often a single-point cutting tool or a boring bar. Movements are made to regulate the depth, size, and hole form to obtain a high accuracy.
3. Rotating and Cutting
After that, the cutting tool revolves around the hole in the machine. The revolving cutter cuts the material from the interior surface, slowly increasing and refining the hole’s size. Further cutting action is performed until the hole has the required size.
4. Finishing the Process
When the throat reaches the correct size, the tool is pulled out. To validate the hole meets the specified dimensions the workpiece is checked. Another modification is made to attain the final polish where the hole surface appears perfectly rounded and is of equal size.
What Are The Disadvantages of Boring Machining
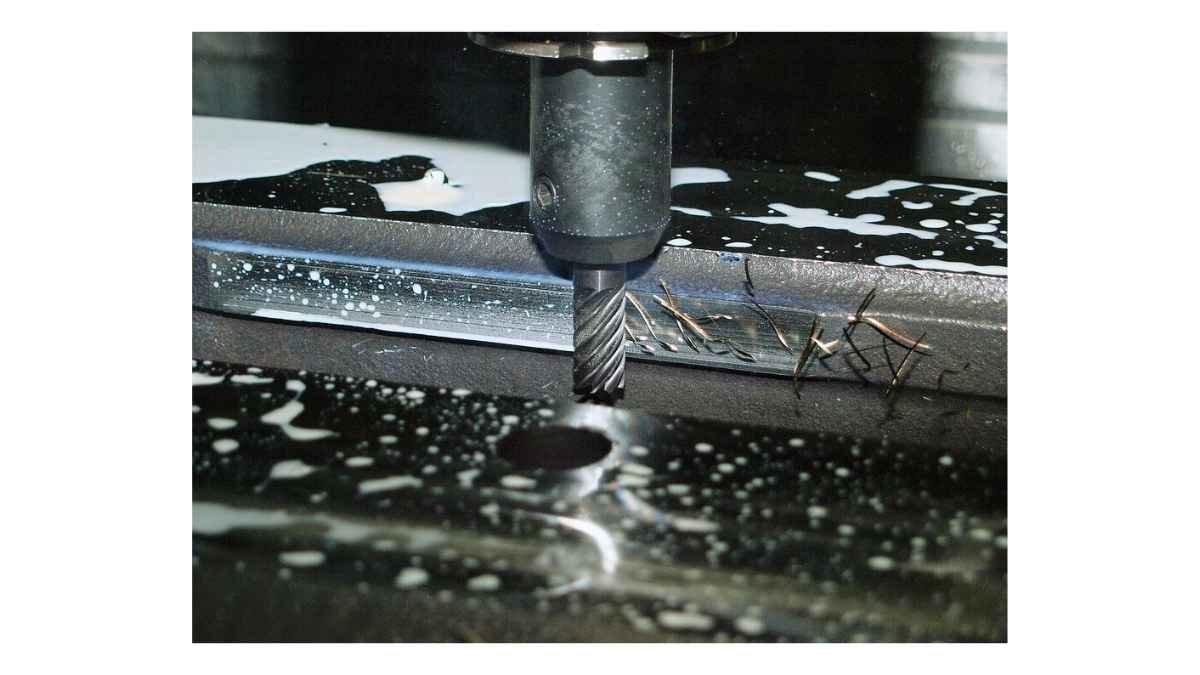

Material Cracking In Boring Machining
Image Description: A close-up of boring machining showing material cracking due to excessive cutting forces
Boring machining can pose certain challenges, including;
1. Slower Process Compared to Drilling
Drilling is often faster than boring machining. The method is slower. It is precise, but it takes time. Unlike the normal practice, the holes are not uniformly close to each other. For large production runs, this slower pace becomes a disadvantage for 3D printing.
2. Higher Setup and Tooling Costs
Boring machining needs specific apparatus and puts initial costs high. Further, the tools employed in boring also undergo wear and tear and require replacement most frequently. This can further augment the process cost to some extent.
3. Comparatively Low Efficiency in Large Scale Production
However, boring is more precise compared to milling. But it’s not optimal for mass-scale production. The limitations that may hinder the achievement of mass production include the time and cost incurred in setting up each job, which can delay the rate of production.
4. Challenges with the More Rigid Artifacts
Boring machines have difficulties when working on hard and abrasive materials. These materials also increase the rate of tool wear and may need a tool replacement. In such instances, other machining operations might be preferable.
5. Not Ideal for Large Holes
Boring is used for perfecting the parts. It’s not designed for swiftly and easily making large holes. Despite this, it’s superb for refining existing holes. However, boring is not optimum for large-hole production in terms of speed and quantity, unlike other machining techniques.
What Are The Advantages of Boring Machining
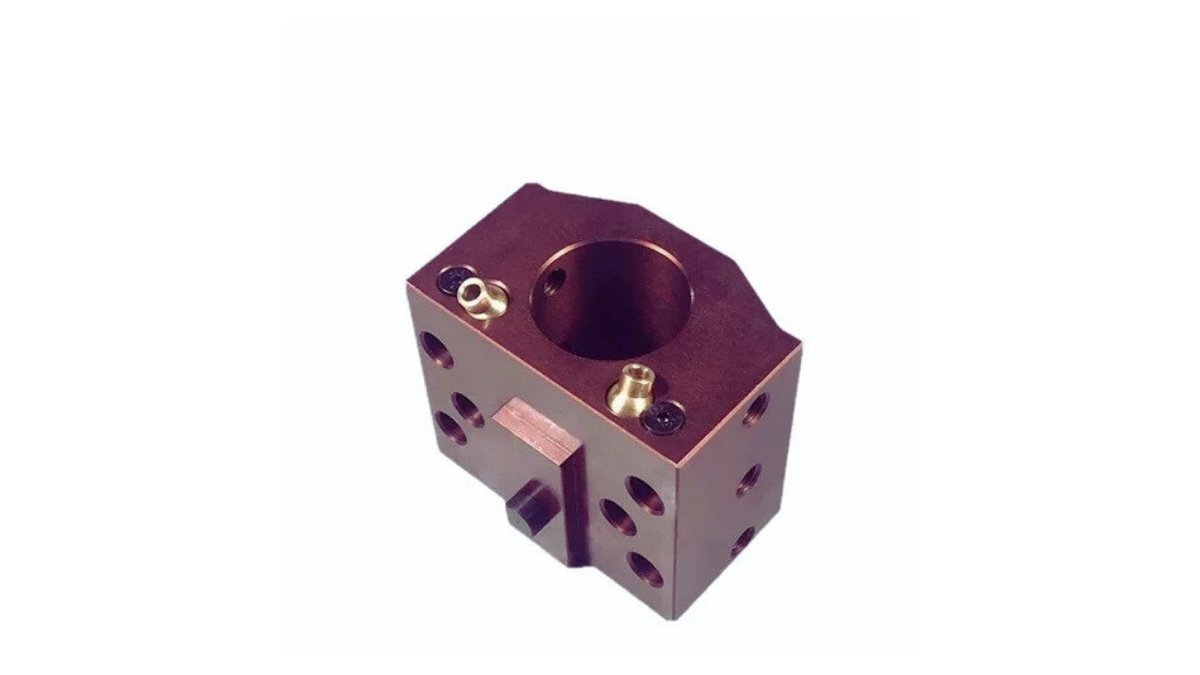

Boring Machined Block
Image Description: An Image of a precision-machined block. It features a smooth, accurately bored hole and highlights ca lean surface finish and tight tolerances achieved through the boring machining process.
- Boring machining provides incredibly precise and consistent hole sizes.
- It allows for better control over the hole shape and finish quality.
- The process creates smooth, polished surfaces, cutting down extra finishing steps.
- Boring is highly adaptable and works well with metals, plastics, and composites.
- It refines holes made by other methods, such as drilling or casting.
- With boring, you can achieve much tighter tolerances than with other conventional techniques.
- The boring process is budget-friendly, especially for high-precision, small-batch parts.
- Boring, moreover, reduces errors, improving overall reliability in critical applications.
Types of Boring Machines
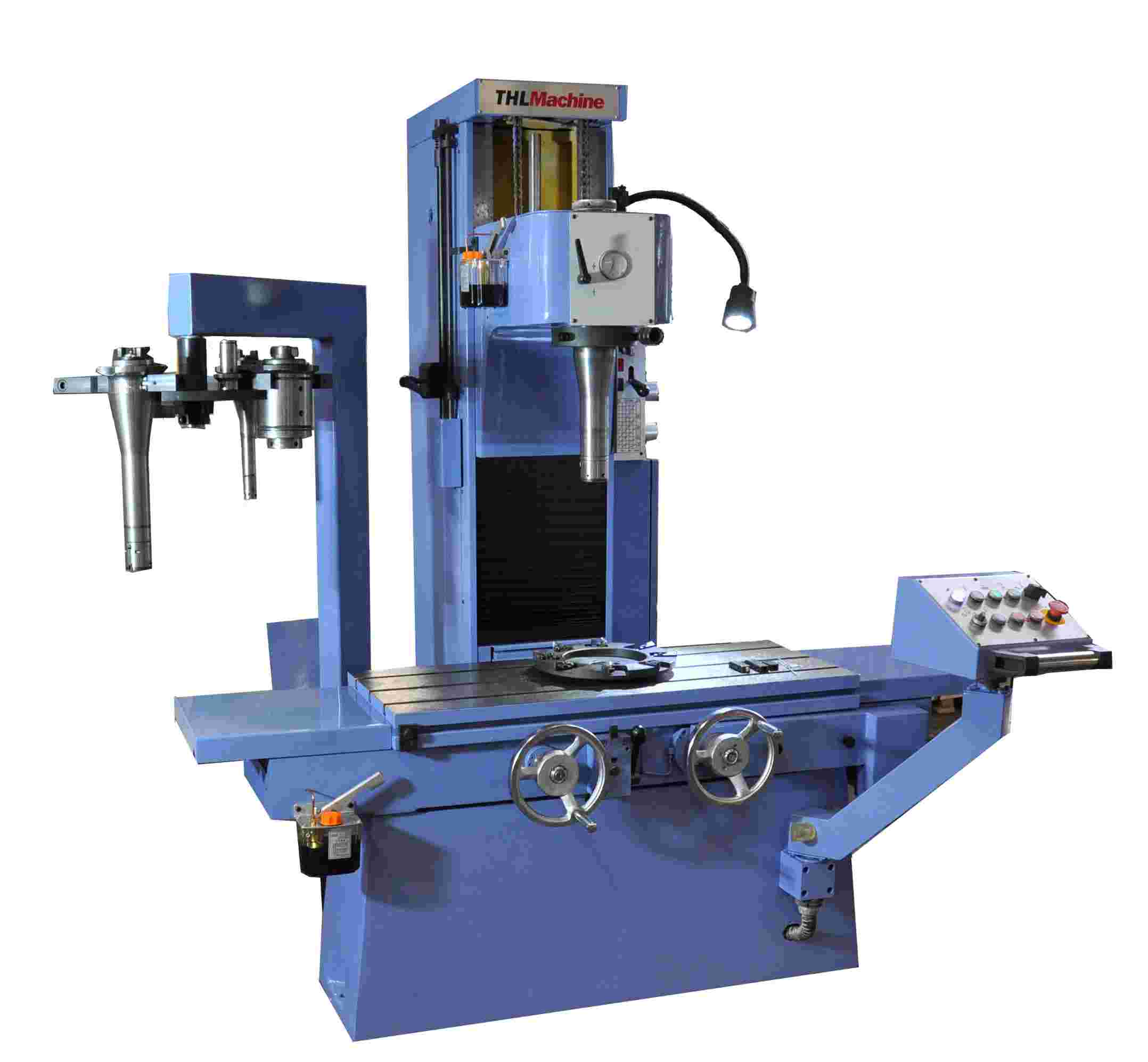

Boring Machine
Image Description: A vertical boring machine standing idle, showcasing its sturdy frame, spindle, and worktable.
The typical types of boring machines include;
1. Horizontal Boring Machine
Horizontal boring machines have the spindle mounted horizontally. This setup allows for larger workpieces to be processed with better stability. They’re perfect for heavy-duty tasks, offering precision in large-scale operations.
2. Vertical Boring Machine
Vertical boring machines feature a vertically aligned spindle. This design is ideal for smaller, more precise boring tasks, such as machining engine blocks. It allows for a high level of accuracy in vertical applications.
3. CNC Boring Machine
Computer numerical control (CNC) boring machines are automated for maximum precision. Controlled by a computer, these machines offer superior consistency and repeatability. They’re widely used for high-volume production and complex designs.
4. Radial Boring Machine
Radial boring machines allow for multi-directional movement of the cutting tool. This makes them highly versatile, and capable of handling larger and irregularly shaped parts. They’re ideal for jobs that require flexibility and high precision.
5. Line Boring Machine
Line boring machines are specifically designed for boring holes in a straight line. These machines are essential for repairs or maintenance tasks, especially in large industrial machinery like engines and heavy equipment. They provide precise alignment for multiple holes in one go.
Applications of Boring Machining
Let’s discuss the common applications of boring machining;
1. Engine Block Manufacturing
Rotary boring can precisely make engine blocks. It allows you to accurately center and size the cylinders. Boring is applied by engineers to signify the engine’s performance and in the long run, to reduce wear.
2. Aerospace Industry
In aerospace, boring is used to make contours in aircraft components. Technicians apply it to achieve the precision needed for complex shapes of such components as turbine blades or engine casing. Such accuracy brings safety and high functional benefits.
3. Oil and Gas Industry
In the oil and gas industry, boring machining is employed in the production process in the making of holes within pipes and drillings. Moreover, it makes sure these parts achieve the needed accuracy to perform well under very high loads. Technicians carefully monitor the accuracy to prevent any failures.
4. Automotive Manufacturing
Boring machining is applied intensively in the car manufacturing industry for components such as transmission housing and brake systems. It validates that parts conform to the exact standards as required. Using boring further improves the strength and reliability of automotive parts.
5. Construction Equipment
Boring is useful in construction equipment since large machinery requires accurate holes. In gear and shaft connections, boring is applied by engineers to guarantee the right fit. The precision enables efficiency as well as durability of the machines used in construction.
6. Heavy Machinery Parts
Many sectors use boring in crafting heavy machine products such as hydraulic cylinders and bearings. Technicians perform boring to achieve the required hole size and improve the functionality of the parts. Optimal boring practice leads to long-lasting machining parts.
7. Tool and Die Making
In tool and die making, operators use boring to achieve maximum accuracy in the positioning of holes, especially in molds and dies. Boring confirms that the parts are accurately fitted and required for high-quality mass production. These bits of accuracy ensure that the overall manufacturing process runs efficiently.
Practical Tips for Optimal Boring Machining
For optimum outcomes in the project, consider the following guidelines;
1. Tools and Their Uses
It’s always important to make the right selection of boring tools for the material being used. The highest quality boring bars mean that you get accurate and clean cuts. To minimize these errors, possible tools should be selected based on the size and required hole depth.
2. Keep the Proper Configuration of Tools
Proper alignment also plays an imperative role. Make sure that your workpiece is heavily clamped down and the tool is correctly positioned in the center of the hole. Because a slight misalignment can result in variations in the slices and dimensions of the hole.
3. Be Careful on Cutting Speeds and Feed Rates
In metal cutting operations, you should always use the appropriate cutting speed as well as feed rate, which normally depends on the material in question. Higher speeds can be used for work on softer materials, while low speeds are convenient for tough materials. A consistent feed rate will give the holes free from tool wear and a smooth surface.
4. Keep Tools Sharp and Well-Maintained
The tool face comes out dull and slows the machining process since it takes more time to complete. You should also check at a regular basis of your boring tools and sharpen them when needed. The maintenance of tools also decreases part defects and helps in increasing the life span of the machines.
5. Use Coolant to Prevent Overheating
Boring tools should be cooled during boring operations. Because they can heat up from friction forces. Coolant prolongs the life span of a tool and enables a more effective cutting to be done. It also minimizes the chances of the material getting distorted.
6. Take Test Cuts Before Final Machining
When working on the last piece of a project, it is always wise to make mock cuts on waste material. Since it helps ensure the tool is performing as expected. Moreover, it helps you set the right machine settings since you can make test cuts and see their results.
7. Check Hole Dimensions Regularly
Periodically, use a micrometer to check whether holes are cut and have the right sizes. The paper found that this assists in identifying errors at a preliminary stage. Most importantly, the high frequency of checks and balances eliminates the possibility of off-spec parts being produced.
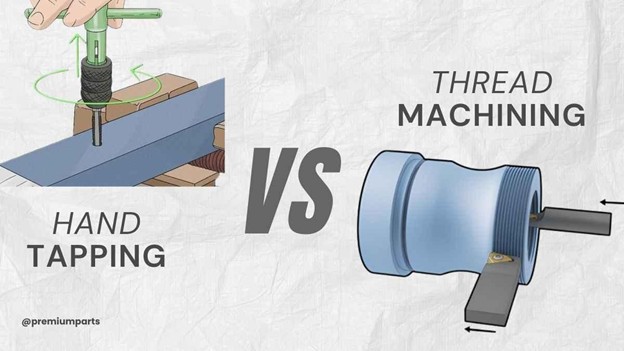
Comparing CNC Boring vs. Drilling
Boring and drilling both create holes, but they serve different purposes. Drilling makes a hole by removing material with a rotating bit. Boring, on the other hand, enlarges or refines an existing hole to precise dimensions. Drilling is faster and ideal for making initial holes, while boring provides greater accuracy for final hole sizing.
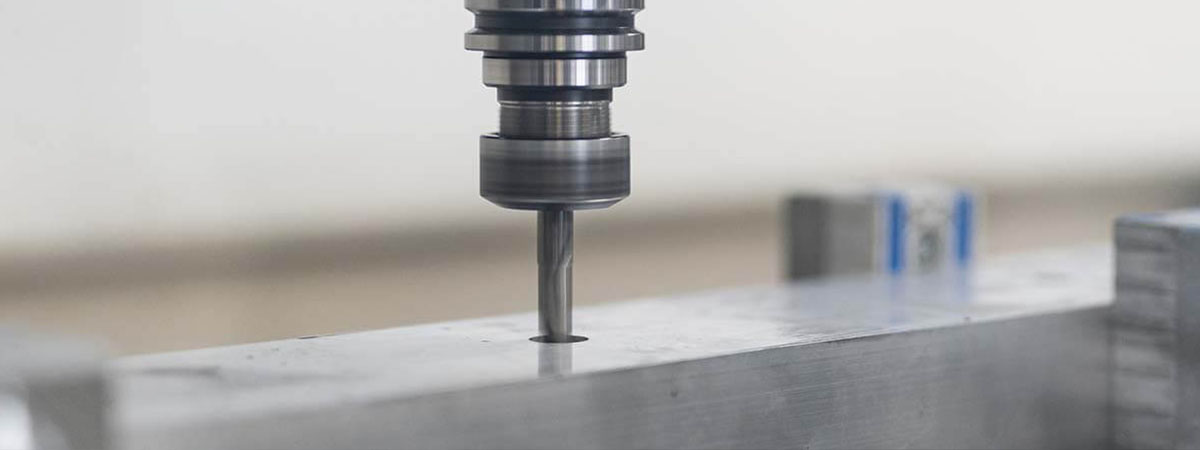

CNC Drilling
Image Description: A CNC drilling process showcasing a rotating drill bit creating precise holes in a metal workpiece.
What Are The Differences Between Boring vs. CNC Turning
Turning and boring are similar but are used for different types of workpieces. Turning shapes the outer surface of a part, while boring focuses on the inner surface, specifically enlarging or smoothing holes. It is great for producing cylindrical parts, while boring is essential for fine-tuning holes with tight tolerances.
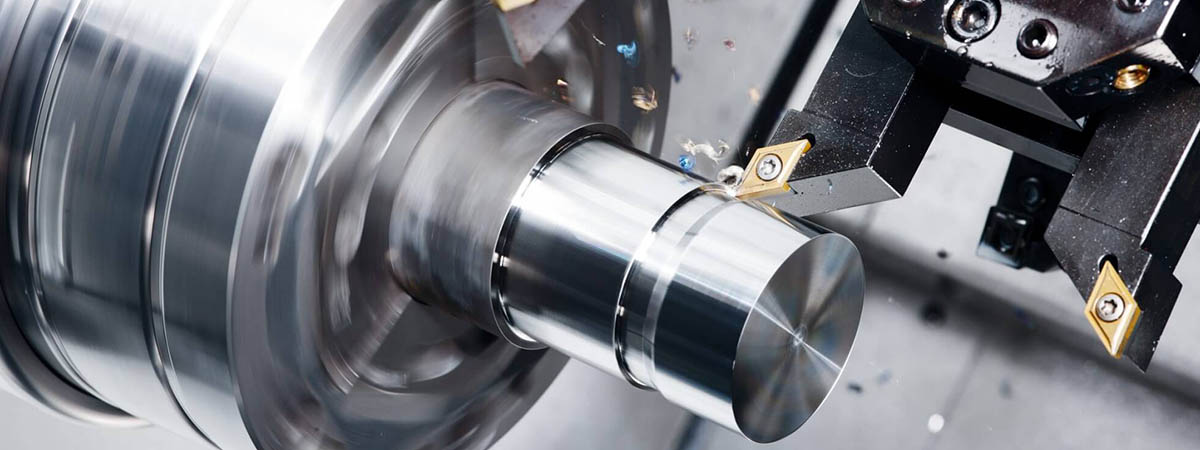

CNC Turning
Image Description: A CNC turning process showcasing a rotating metal workpiece being shaped by a fixed cutting tool.
CNC Boring vs. CNC Reaming: Key Differences
Boring and reaming are both used to refine holes, but they have different functions. Normally, boring creates or enlarges a hole, ensuring it’s the correct size. Reaming is typically used after boring to improve hole quality, providing a smooth finish and precise diameter. Reaming works best for fine-tuning already bored holes.
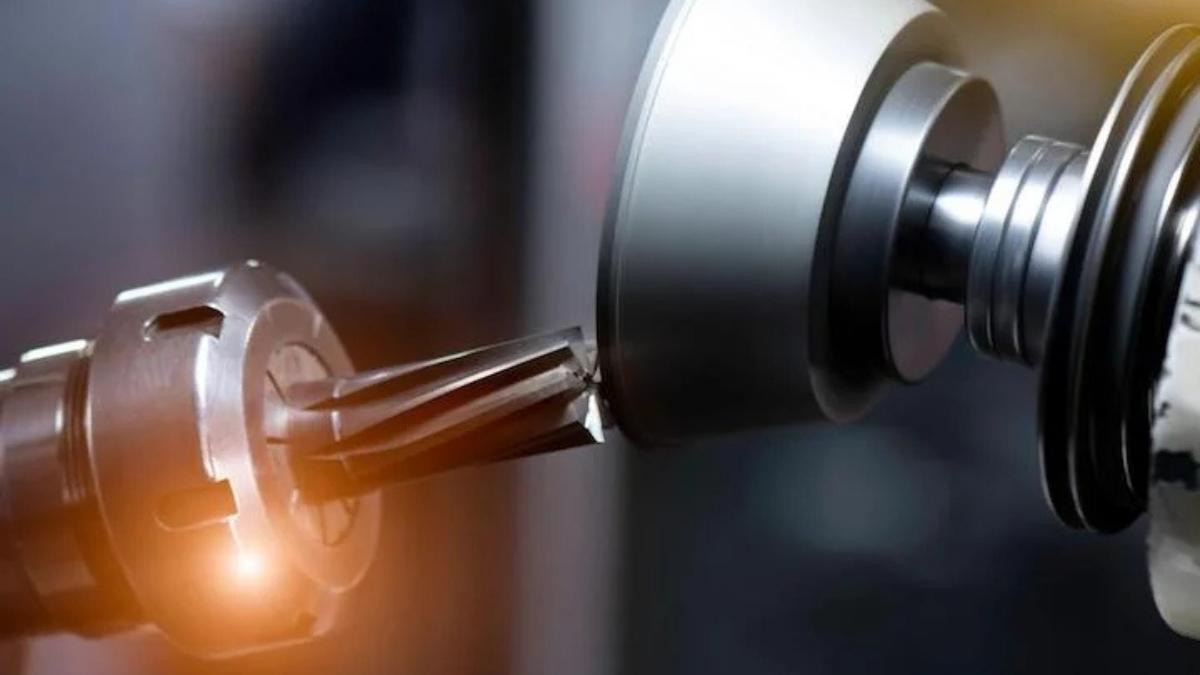

CNC Reaming
Image Description: A CNC reaming process showing a reamer tool precisely enlarging and finishing a drilled hole.
Typical Examples of Boring Tools
- Boring Bar
- Indexable Boring Tool
- Adjustable Boring Head
- Solid Boring Tool
- Tubular Boring Tool
- Carbide Boring Tool
- Fine Boring Tool
- Boring Tool Holder
- Face Boring Tool
- Deep Hole Boring Tool
Materials That Can Be Effectively Machined Using Boring
- Steel
- Stainless Steel
- Aluminum
- Cast Iron
- Copper
- Brass
- Titanium
- Plastics
- Composites
- Nickel Alloys
Conclusion
Boring machining plays an indispensable role in achieving precision and accuracy in various manufacturing processes. While it requires specialized equipment and can be slower than other methods like drilling, its ability to refine and enlarge existing holes with tight tolerances makes it integral for high-quality parts. From automotive to aerospace, boring allows components to meet exact specifications and perform reliably under demanding conditions. By understanding the different types of boring machines and their applications, you can select the right tool for the job and improve your machining process, resulting in better performance and longer-lasting products.
FAQs
Q1. What is the main difference between boring and drilling?
Boring refines and enlarges existing holes, while drilling creates the initial hole. Additionally, boring is more precise and ensures tighter tolerances.
Q2. How do I choose the right boring tool for my project?
Choose the boring tool based on material type, hole size, and desired finish. The correct tool geometry and coating will optimize performance.
Q3. Can boring be used on all materials?
Boring can be used optimally on metals, plastics, and composites. For hard or abrasive materials, special tools or slower speeds may be needed to reduce wear.
Q4. What are the key advantages of CNC boring machines?
CNC boring machines offer high precision and automation. They are perfect for complex, high-volume jobs requiring consistent outcomes.
Q5. Why is coolant necessary in boring operations?
Coolant helps prevent overheating and reduces friction. It also improves tool life and ensures smooth cuts, especially with metal materials.