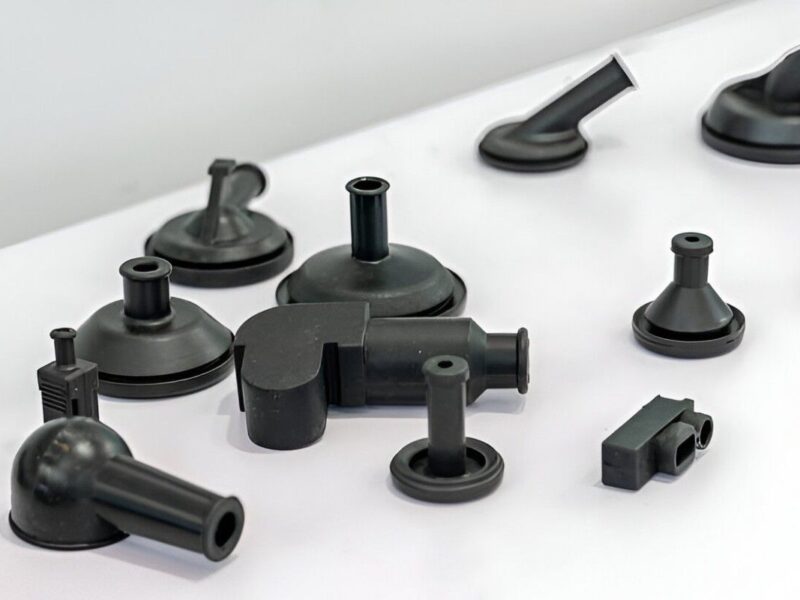
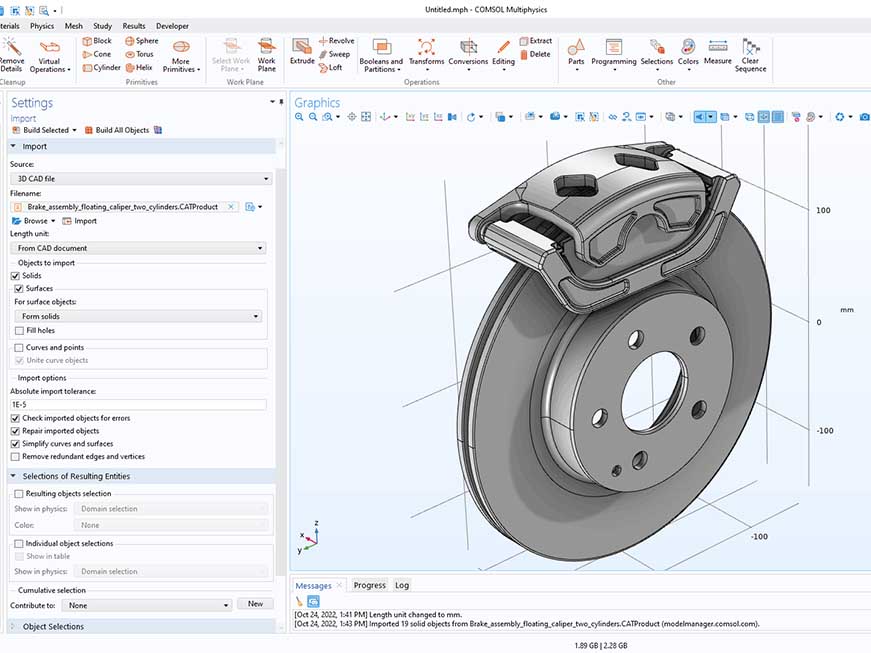
Low volume injection molding is a quick production process for plastic parts. It is commonly used for the development of prototypes that have matured to the testing stage. Moreover, it provides a bridge between early prototyping and mass production of hundreds of thousands of units. It also allows plastic part manufacturers to meet market demand by producing smaller quantities and providing consistent quality.
Premium Parts operates differently from most low-volume injection molding companies. Usually, manufacturers use injection molding for mass production because of the costly tooling. However, new methods now change that. Moreover, production of high-quality, repeatable prototypes is also possible with the use of benchtop or industrial machines. Thus, the method accelerates product development, reduces costs, and shortens lead times.
This guide outlines low-volume molding tools, discusses the process, and explains when to utilize low-volume molding.
What Is Low Volume Injection Molding?
Low-volume injection molding is a high-precision manufacturing process and produces a range of 100 – 10,000 plastic parts. It requires soft or semi-hardened steel molds to produce high-quality parts consistently with tight tolerances. Unlike 3D printed parts or aluminum molds, steel tools are more durable and suitable for complex geometries. Therefore, it’s a great way to create functional prototypes, bridge productions, and test the market!
Moreover, manufacturers enjoy lower tooling costs, shorter lead times, and dependable repeatability. By using low-volume injection molding, you are shortening development cycles, reducing risk, and getting products to market faster. In addition, it is very cost-effective to produce durable parts – parts that are ready for testing – that have production quality.
Low Volume Injection Molding Vs. Traditional Injection Molding
Injection molding is one of the most accurate and precise methods to manufacture plastics. The small quantity injection molding uses steel or 3D-printed molds and eliminates the high costs. Besides, it uses molten material inside the mold to shape the product. The popular materials include ABS, PS, PE, PC, or TPU.
In contrast, traditional production processes require expensive molds made from metal and produced from CNC machining or EDM, with a lead time of 4–8 weeks, which costs $2,000 to over $100,000, and is not suited for small-batch production.
Alternatively, low-volume injection molding can offer faster turnaround periods with soft tooling or digital fabrication. Therefore, manufacturers are now using on-demand manufacturing platforms with real-time quoting, order tracking, and greater visibility throughout their supply chain.
Low-volume injection molding suits well for prototyping, bridge production, and custom runs. However, traditional molding is suited for mass production and consistent designs. Besides, short-run plastic injection molding also leverages Industry 4.0 technologies: Big Data, cloud platforms, and automation. These technologies help with smarter, cost-efficient product manufacturing.
Nonetheless, the outcome includes quality, repeatable parts, taking tighter tolerances, and much shorter design cycles. This advanced technique gives engineers the ability to iterate, cut expenses, and respond to market scenarios faster.
Are you ready to manufacture parts at speed, precision, and flexibility? Get your quote today from Premium Parts and speed up your next project with our small part injection molding!
Workflow of Low-Volume Injection Molding
Injection molding includes different steps for part manufacturing. So, if you are searching for “plastic injection molding near me,” skip the hassle right now and learn about our process. Then contact our professionals at Premium Parts to get a quote. Our low-volume injection molding process includes:
Mold Design
The first decision you need to make is to define the specifications of the final part and choose the appropriate material. Your material selection will have an immediate impact on mold design and the performance of the part. Nevertheless, metal and aluminum are the most common materials used for injection molds because of their machinability.
Design your mold using CAD software that fits your workflow and technical needs. Follow standard design principles for injection molding and additive manufacturing to avoid defects. Ensure proper draft angles, wall thickness, and gate placement. Similarly, for polymer 3D-printed molds, apply specific guidelines to ensure structural integrity and print success.
Mold 3D Printing
Engineers build a prototype using 3d printing, typically referred to as a 3D printed mold. After it is printed, they evaluate it to ensure there are no design or functionality issues. Then, if there are flaws, they will adjust the design as needed and either print a new part or make edits using the CNC machining method.
To create a 3D printing mold, you need to select the right material by checking its strength, accuracy, and thermal resistance. Rigid 10K Resin, printed at 50-micron layer height, is ideal for most mold designs. Moreover, it offers excellent stiffness, durability, and heat tolerance.
When printing, always orient the mold flat on the build platform with no supports to minimize any warping. After printing, wash and post-cure the mold for optimal mechanical properties. Your 3D printed mold is now ready to use for the injection molding process.
Mold Assembly
Before assembly, utilize either hand-sanding or CNC machining to complete the mold to adhere to tight tolerances. If you would like to add strength, put the 3D printed mold into a typical metal frame or Master Unit Die. This will protect the 3D printed mold from high injection pressures and will also improve the mold life.
Handle the printed mold carefully to fit into the frame. Add in places for the ejector pins, inserts, side-action parts, and any other design features required based on the part design to use the printed molded part molding setup procedure.
Moreover, assemble the entire mold into your low-volume injection molding machine. Subsequently, set the rest of the machine to parametric settings for temperature, pressure, and injection speed. Load the ejector system inside the mold before adding it to the mold.
Mold Clamping
Use a clamping mechanism to keep your mold in a secure position during the injection cycle. The clamping mechanism applies a loading force to close the distance between the two halves of the mold. This loading force must equal the injection pressure used to keep the mold from opening or shifting.
Use less clamping force for 3D printed molds in metal frames. When you apply less clamping force, it places less stress on the printed material and maintains part quality. It is important always to use a balanced clamping force and ensure that the clamping force stays in line with the mold strength and machine parameters.
Injection and Cooling
This process varies depending upon machine type, but every method involves injecting molten plastic into the injection barrel. Subsequently, the injection machine injects the molten material into the mold cavity, maintaining controllable speed and pressure.
Once injected, the plastic turns to liquid and begins the cooling and solidifying phase of the molding process inside the mold. The cooling time depends on the material of the mold. Besides, the cooling time for plastic molds occurs more slowly than the cooling time for metal molds due to the thermal conductivity of the materials.
Demolding
Take the part out of the mold system, either automatically using ejector pins or manually. Manual demolding is an excellent option for simple parts in low-volume injection molding.
When demolding the part automatically using ejector pins, the clamping plate moves out of the way, allowing the mold halves to separate. Consequently, the ejector pins push the molded part out of the mold. Use a release agent when processing high-viscosity thermoplastics to facilitate demolding, as well as for the protection of the mold.
Applications of Low-Volume Injection Molding
Small part injection molding has three major applications when it comes to low-volume production. Here are the details of each application:
Rapid Prototyping with Injection Molding
Low-volume injection molding is ideal for prototyping plastic parts. It reduces the time and cost of producing functional prototypes. Engineers can easily prototype, test, validate, and modify their designs in low volume before committing to full-scale production. As a result, this eliminates unnecessary design errors and shortens the development cycle.
Short-run Plastic Injection Molding
This method allows for small production sizes without the cost associated with second-generation molding. This is practical for startups and businesses with limited capital. Besides, small batch injection molding is a rapid-response, low-cost way to introduce products to market.
On-Demand or Custom Injection Molding
On-demand molding will only produce parts as they are needed, significantly reducing inventory and storage costs. It provides a new way of enabling flexible manufacturing during periods of changing demand or robust demand variability.
Moreover, businesses can adjust production levels as necessary as demand changes in real time, reducing waste and increasing efficiency for resources.
Are you looking to prototype, scale, or stay agile with production? Explore our injection molding solutions with plastic today.
Types of Thermoplastics for Small-Quantity Injection Molding
Choosing the right thermoplastic is critical to success for low-volume injection molding; each thermoplastic has its own unique mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties. Additionally, the engineer must associate material properties with the functional requirements of parts, environmental conditions, and processing conditions.
| Thermoplastics | Properties | Applications |
| Acrylic (PMMA) | Transparent, rigid, scratch-resistant, UV stable | Ideal for optical parts, light covers, and display windows. |
| Acetal (POM) | Strong, low-friction, dimensionally stable | Used for precision gears, clips, and automotive components. |
| Delrin (POM) | A branded acetal with high stiffness, fatigue resistance | Performs well in load-bearing, high-wear applications. |
| Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) | High strength, heat-resistant, and good electrical insulation | Common in electrical housings, connectors, and automotive sensors. |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | Impact-resistant, transparent, heat-resistant | Excellent for protective covers, lenses, and enclosures requiring toughness. |
| ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) | Tough, good surface finish, moderate strength | Versatile and widely used for enclosures, toys, and appliance parts. |
| Nylon (PA6/PA66) | Tough, abrasion-resistant, moisture-sensitive | Suitable for gears, bearings, and structural parts under stress. |
| Polyethylene (PE) | Flexible, chemical-resistant, low moisture absorption | Best for containers, tubing, and parts needing chemical durability. |
Benefits of Low-volume Injection Molding
Low-volume plastic injection molding offers several important benefits that make it a favorable option over traditional methods, particularly when it comes to low-volume high-quality plastic parts. Below are its main advantages:
- Uses Softer Aluminum Tooling: Low-volume molding utilizes aluminum, rather than hardened steel, which promotes faster and simpler mold making. Aluminum readily accepts surface treatments and does not require annealing like steel will.
- Quality Parts Manufacturing: Despite the use of softer molds, it allows for good quality and functional parts with good dimensional accuracy. The great heat transfer associated with aluminum also improves cooling time and allows for complex mold designs.
- Save Costs: Manufacturers can make low-volume batches that do not require a minimum order, which reduces inventory costs and waste. Therefore, low-volume injection molding is a great option for a startup and testing products.
- Shorter Lead Times: Aluminum tooling speeds up mold fabrication, reducing total production time by significant amounts of time. Quicker mold delivery and smaller production volume also mean a faster time to market.
- Flexibility in Design: Supporting production in small runs allows for easy design changes with no major cost or delay impact, and is more conducive to iterative development and validating the design early.
- Bridge for Scale: Low-volume injection molding fills the gap between prototyping and high-volume production. Moreover, it provides quick transitions, process refinements, and assurance when scaling with less risk.
How Much Does Low-volume Injection Molding Cost?
The price of low-volume injection molding will vary for each project depending on the complexity of the part, the type of material, and the tooling type used. Mold costs are on average between $1,500 and $15,000, depending on the design, number of cavities, and tolerances.
Using aluminum or 3D-printed molds results in substantial savings in tooling costs when compared to steel molds. While the part cost generally ranges from $1 to $10, it could exceed those amounts for parts with complex geometries or specialty resins.
Additional cost factors include:
- Material selection (thermoplastics like ABS, PC, POM, etc.)
- Mold complexity (multi-cavity, inserts, side actions)
- Part size and volume
- Post-processing or secondary operations
- Lead time and turnaround speed
Low-volume injection molding saves on upfront costs to prevent overproduction of a part asymptotically. Thus, it serves as a cost-effective solution for prototyping, bridge production, or small-batch launches.
Premium Parts – The Best Low-volume Injection Molding Parts Manufacturers
For premium quality high-volume production, Premium Parts is one of the reputable low-volume injection molding manufacturers. Our team can work in small runs, deliver high-quality, durable, precise, and cheap parts. Specializing in small-batch production, they utilize advanced technologies, including desktop injection molding machines, to provide precision parts quickly and affordably. Whether you need quick prototypes, bridge production, or on-demand production, Premium Parts provides reliability and confidence with faster lead times.
Moreover, we offer a variety of thermoplastics to support any tool, and we will always develop tools that produce the best results for your project. So, if you’re looking for flexibility without sacrificing speed and quality while avoiding the expensive traditional tooling costs, Premium Parts is your partner in manufacturing.
Final Thoughts
Although traditional injection molding is the best method for production at a large scale, low-volume injection molding provides small and medium-sized companies with the ability to create small quantities without the exorbitant capital investment.
It provides faster access to the market, improved product testing, increased design variation, and better lead times. Moreover, you can get a greater level of mobility for a business to be flexible and reduce risk while remaining efficient in manufacturing ideal products. Thus, try low-cost injection molding today and make better choices.
FAQs
What makes Premium Parts the best Low-Volume injection molding manufacturer?
Premium Parts is a provider of commercial-grade parts with quick turnaround, competitive pricing, and awesome part quality using advanced technologies, including desktop injection molding machines. Besides, they specialize in low-cost injection molding, which is perfect for prototypes and small batches.
Are There Any Alternatives to Low-Volume Plastic Injection Molding?
Yes, options include CNC machining, 3D printing, and urethane casting. Although CNC machining and 3D printing are appropriate options for both small batches and complex shapes, they may have different material options or surface finishes, and other cost structures as well.
How to Choose the Right Partner for Plastic Injection Molding Near Me?
Seek a manufacturer who has a good reputation, quick lead times, tooling on-site, and strong pricing. Moreover, look for reviews and case studies, and make sure that they are offering prototyping and low-volume production.