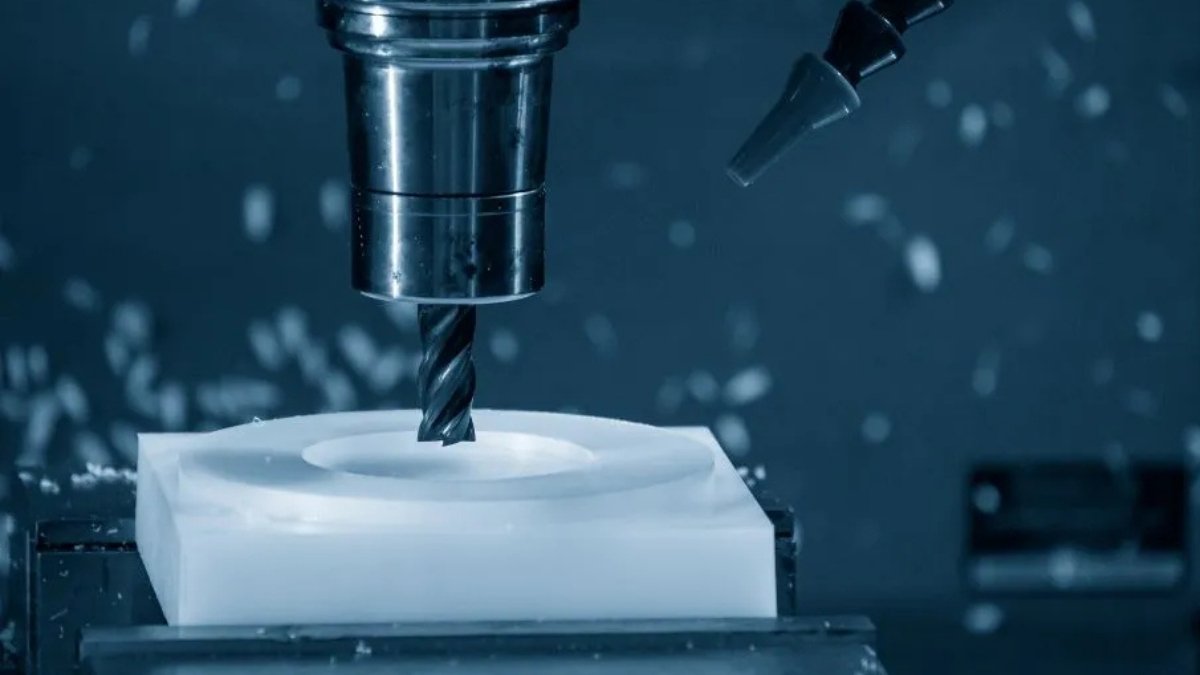
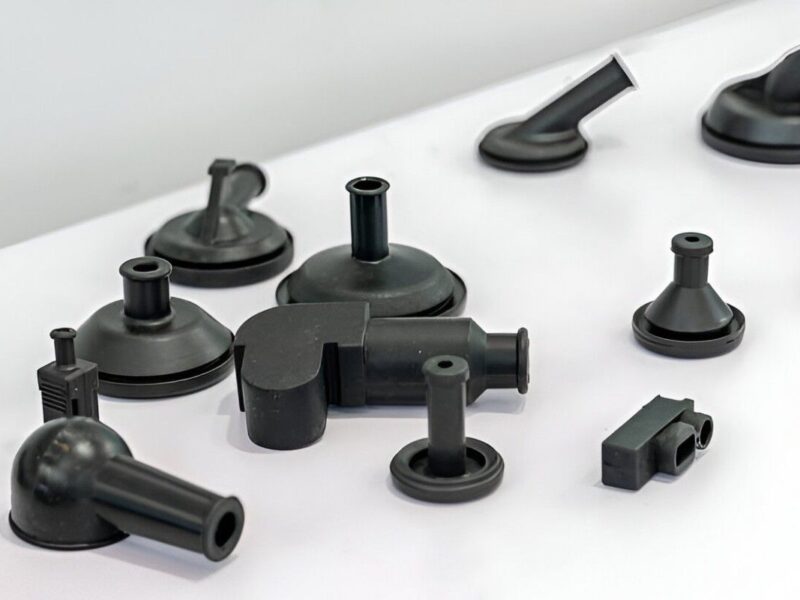
CNC Machining of ABS Plastic Sheet
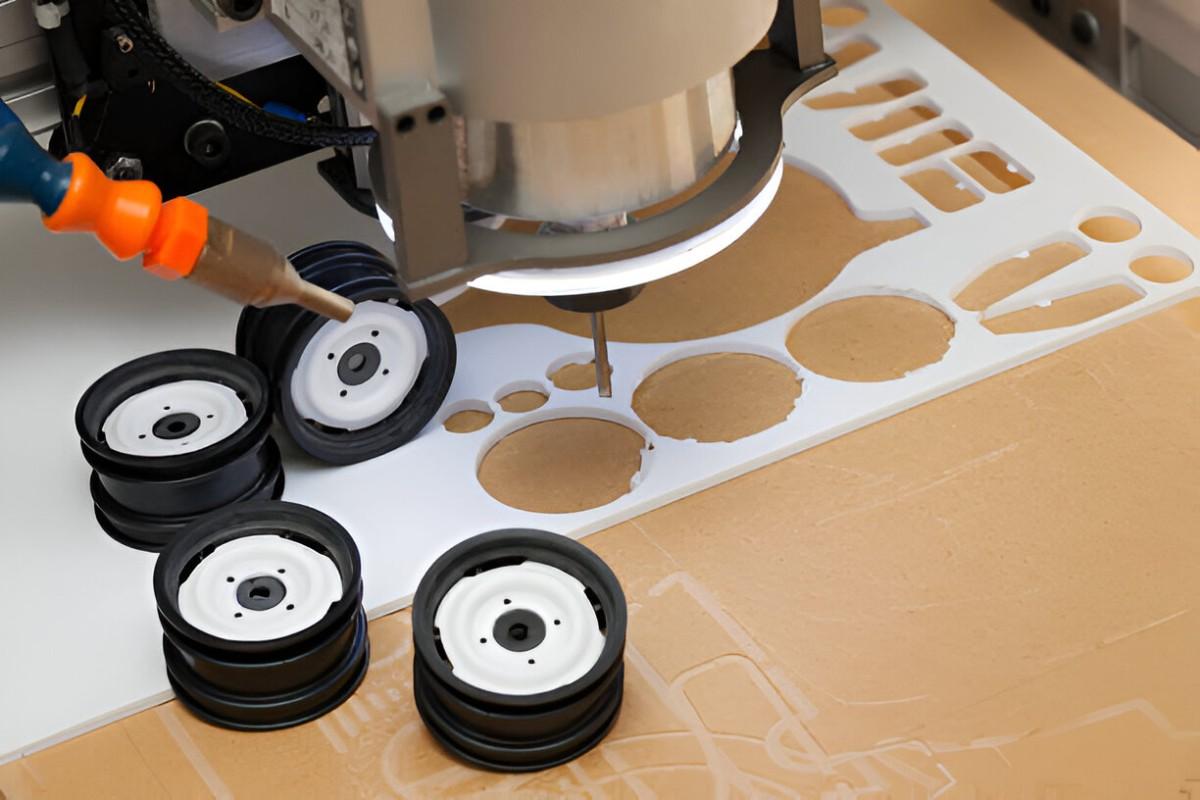
CNC Machining of ABS Plastic Sheet
Image Description: The image shows an ABS plastic sheet being precisely machined to produce prototypes.
Plastic product manufacturing is a very versatile process. Because of parameters such as function, quality, and volume, a number of methods may be best suited for specific batches of production over others. Today, we take a quick look at the various manufacturing methods available to create your product parts in different volumes.
1. Low-volume Manufacturing
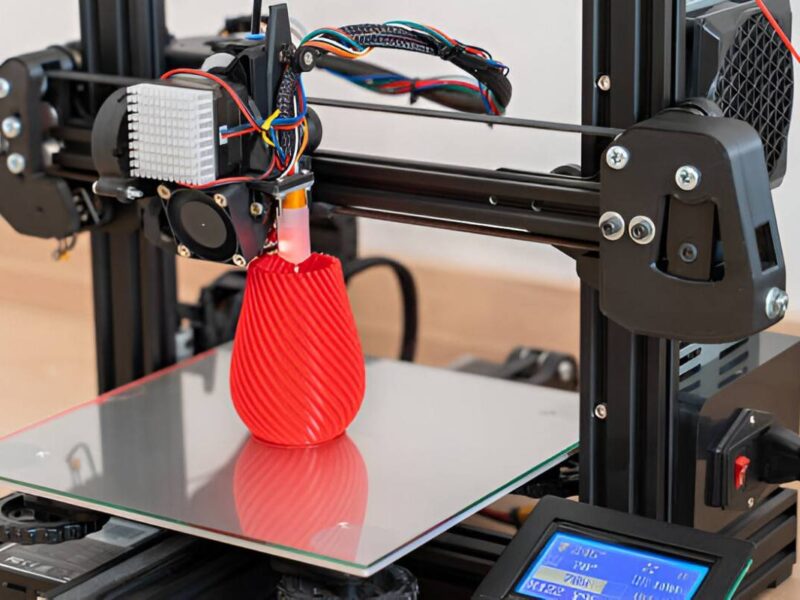
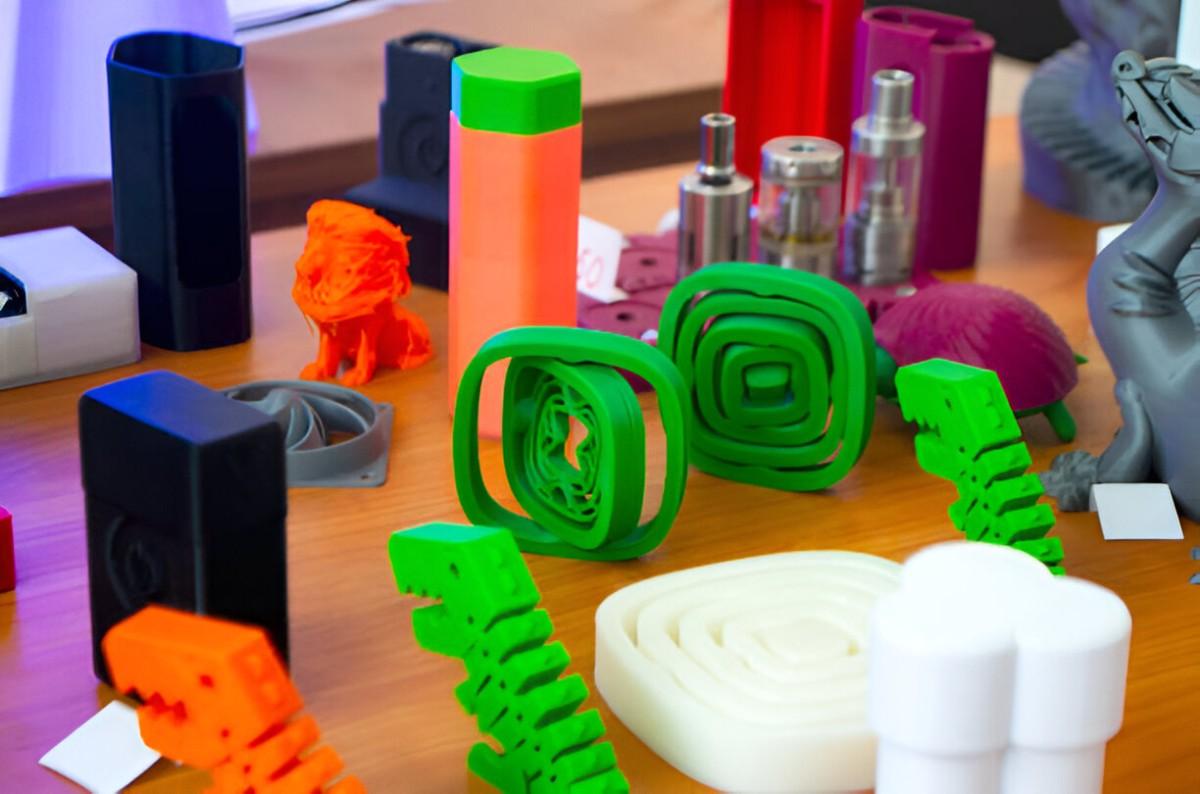 Multicolored 3D Printed Models
Multicolored 3D Printed Models
Image Description: A close-up of Multicolored 3D printed models displayed on a table.
Low-volume manufacturing generally covers the manufacturing of plastic parts within the range of 10 to 100 units. For low-volume manufacturing, we may consider CNC machining and 3D printing.
CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing technique that uses digital/computer-assisted machining software to shape a block of material through drilling and milling processes to remove excess material and form the final product.
We may use 3D printing for low-volume manufacturing to use a computer machine (and a 3D-designed model) to create and piece together the desired shape of the final product from a pool of material. 3D printing is a form of additive manufacturing, and the process is essentially the opposite of the CNC machining process.
These two techniques are often best used for low-volume manufacturing to manage profitability and reduce setup or running costs in your project.
2. Medium Volume Manufacturing
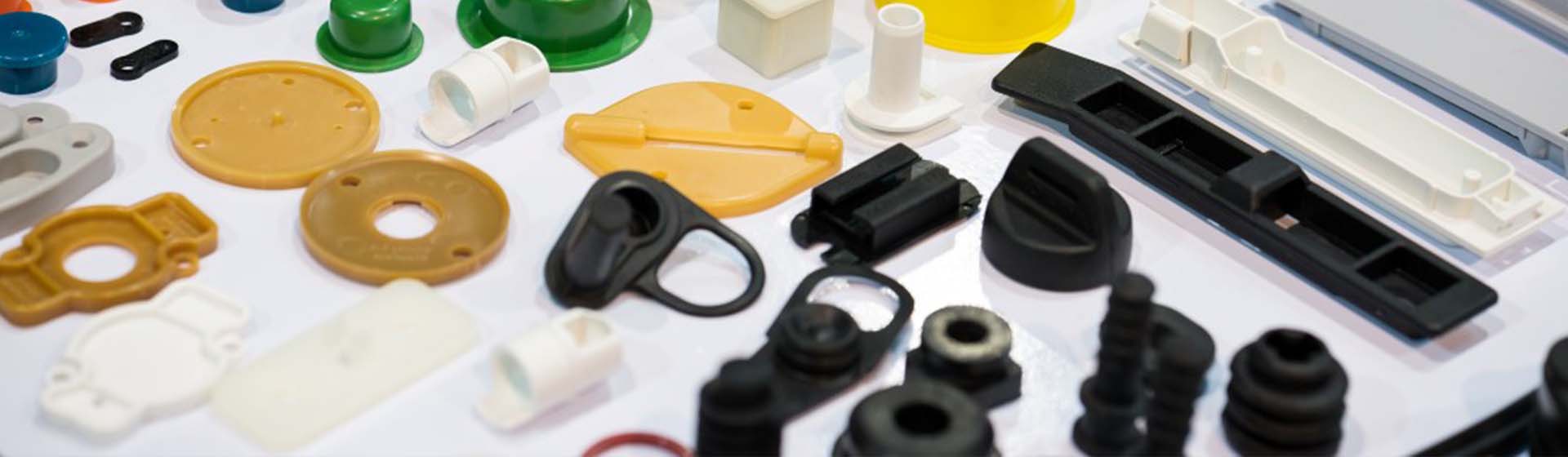
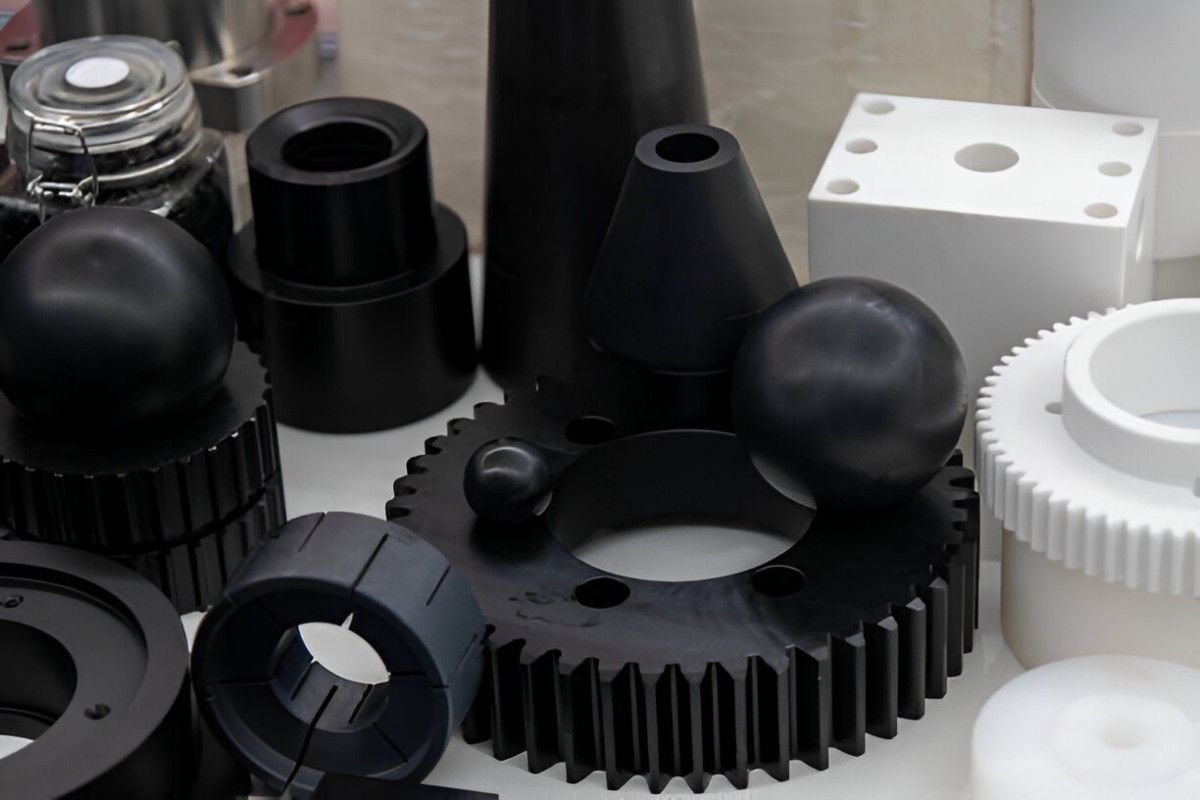 Various Black Plastic Components on Display
Various Black Plastic Components on Display
Image Description: Various black plastic components on display in an industrial setting.
Medium volume manufacturing at Premium Parts will typically involve volumes within 100 to 1,000 units. In cases like these, it is crucial to get the design, molding, and shaping very accurate. When producing this range of unit parts, we employ techniques such as casting, rotational molding, compression molding, and thermoforming.
Thermoforming involves heating plastic sheets into a malleable state and vacuuming the plastic into the shape of a mold. The formed plastic part is then trimmed to arrive at the final desired product.
Another method used in medium-volume manufacturing is casting. When casting, the plastic material is heated to a liquid form and poured into the mold to solidify. The casted part is then removed or ejected from the mold. While casting may sound similar to injection molding and extrusion, the key difference here is that casting uses atmospheric pressure to fill the mold as opposed to the use of actual force in the case of molding and extrusion.
We may also use compression and rotational molding techniques to manufacture medium-volume quantities of your plastic parts. Rotational molding is best suited for significant, single-piece hollow parts. It is done by introducing the molten plastic material into a large mold, and rotating the mold continuously until a hollow shape is formed. The rotational action melts and disperses the resin to fill and coat the walls of the mold. There is no limit to the size of the molding, and this process is relatively inexpensive.
Compression molding is a medium to high-volume, high-pressure technique used in making complex, highly durable plastic parts. The process starts with pre-heating the resin and placing it in a heated mold cavity. There is then a use of force and pressure to bring the heated resin and mold cavity into contact, fill, form, and cure the end product. The heat and pressure must remain constant during the process.
Compression molding is relatively inexpensive when compared to injection and transfer molding. It is material optimal, leaving very little waste, which is an advantage when working with considerably costly materials.
3. High-Volume Manufacturing
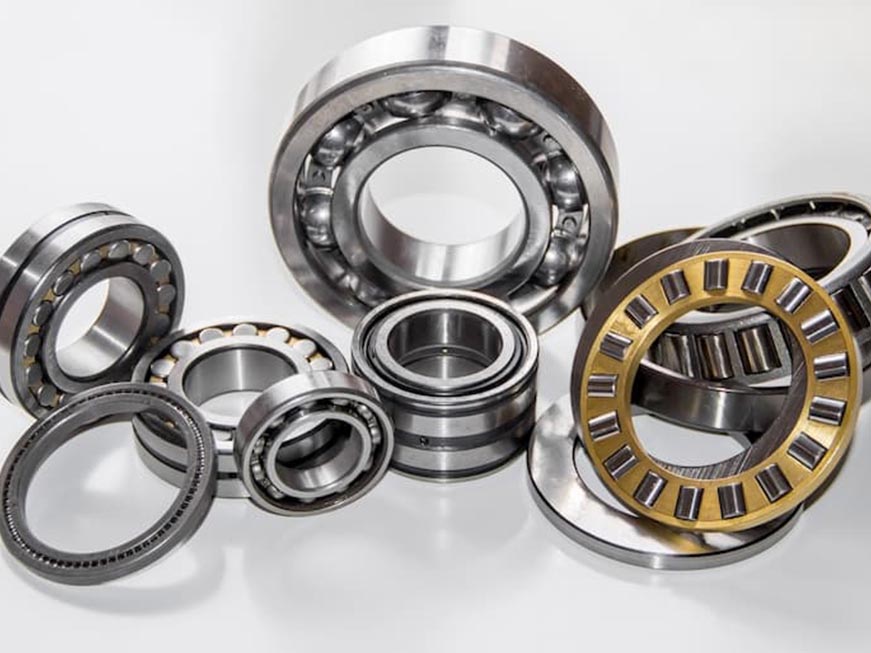
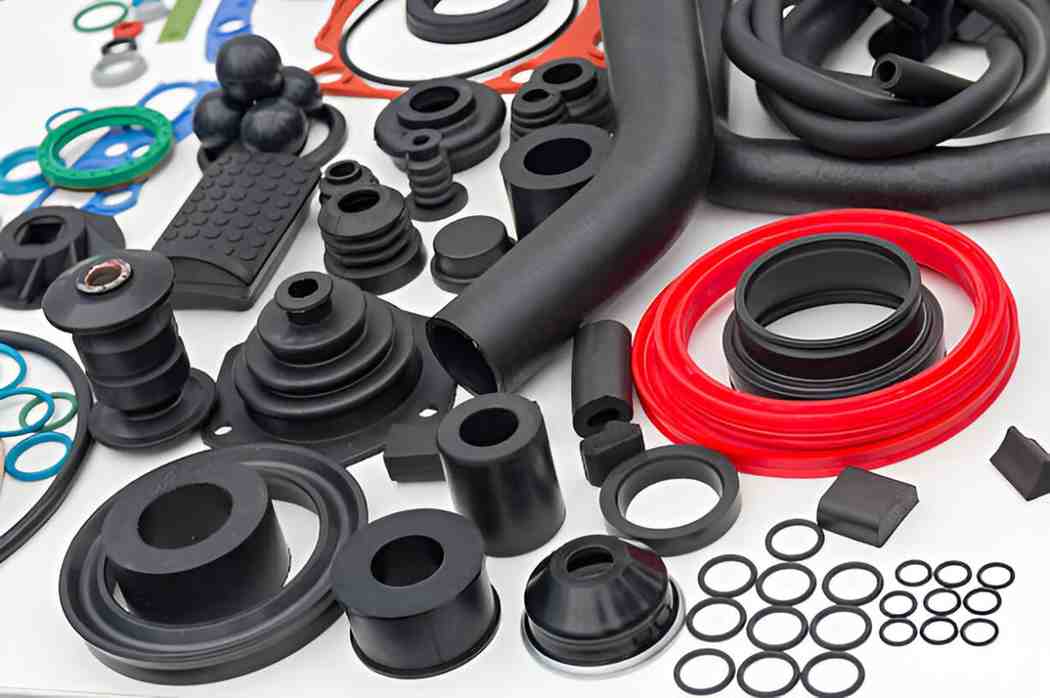 High Volume Plastic Components
High Volume Plastic Components
Image Description: Plastic Parts in considerable volume displayed on a white background.
High-volume manufacturing often requires advanced production techniques that can deliver high-volume molded parts without compromising quality. These methods will often use large machines and equipment in their mass manufacturing.
The standard methods for high-volume manufacturing (100,000 and above parts) include extrusion molding, injection molding, blow molding, and compression molding (already covered above in medium-volume manufacturing).
Blow molding is a plastic production process used in the manufacture of hollow plastic parts. In blow molding, a molten tube (also called preform or parison) is heated and inflated with compressed air till it fills the mold, cools, and forms the shape of the desired product. The difference between blow molding and injection molding is the way they are used. For hollow products like bottles is blow molding is used, while injection molding produces solid plastic products.
Extrusion molding
Extrusion molding is a plastic manufacturing technique to produce high-end plastic parts by pushing molten plastic through a 2-dimensional die opening to form a molded product. The shape of the die is the shape taken by the tube. The extruded plastic is allowed to cool and form the desired shape. Extrusion molding is often used for sheets, films, pipes, hoses, straws, rods, fiber optic cables, and wire coverings.
Injection molding is one of the most popular methods for high-volume manufacturing. This process generally involves heating plastic material into a melted resin and then injecting this into a 2-part mold to cool, solidify, and form the molded part.
High-Quality Plastic Part Manufacturing in China
Premium Parts provides high-quality plastic manufacturing across a wide range of volumes. We are always on board to advise on the best manufacturing methods to proceed with, depending on the end-use, volume, and design specifications for your product. Our engineers are well-versed in all the suitable production techniques to ensure that we deliver excellent parts that are optimized for running your project. Get in touch with an expert and receive a free quote on your project now!