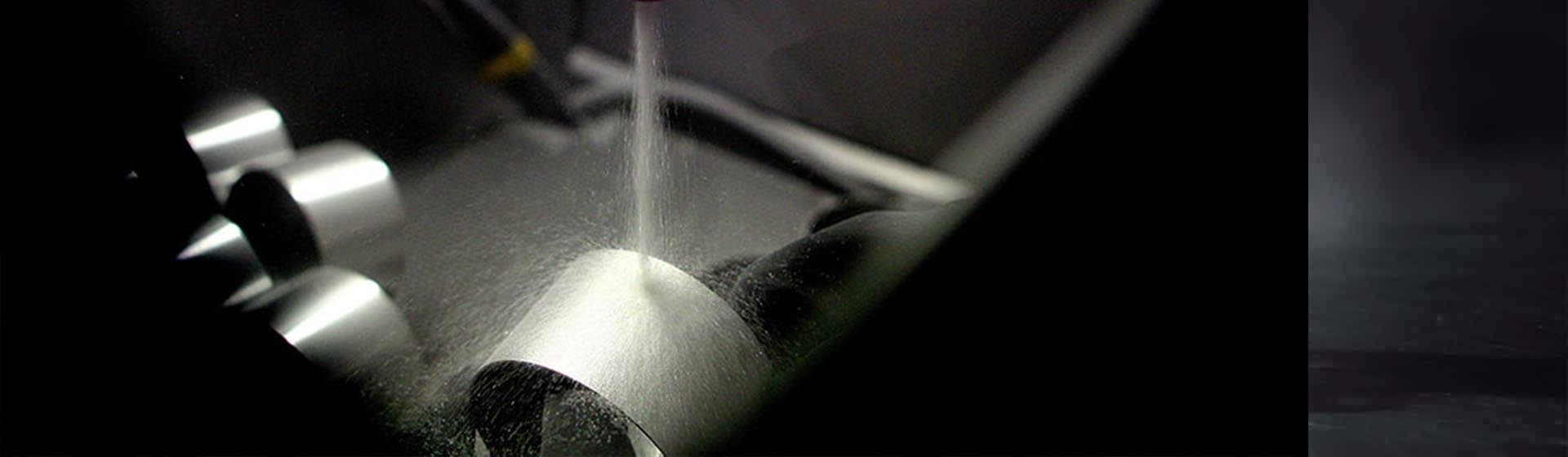
Bead Blasting is a surface treatment for metallic parts/products. In operation, machinists propel tiny materials onto the substrate surface at high velocity to make it rust-free and long-lasting. It is mainly used in the aerospace, automotive, and electronics sectors. Since surface quality is a critical concern in these sectors, manufacturers often face issues with rough surfaces. Thanks to bead blasting, it provides a smoother surface, reducing the need for extensive post-processing and increasing the material’s performance and longevity.
Why Choose Bead Blasting?
Manufacturers perform bead blasts using angular or spherical glass or ceramic beads. They project beads onto the surface of the metal with high pressure to remove unwanted dust and rust from the surface. As a result, the process improves the automobile machinery surfaces, providing a proper finish and flawless end products. Besides, industries like aerospace, electronics, and energy use blasting as a core process to add aesthetic value to products.
Bead Blasting Process: Steps Involved
 Bead Blasting Process
Bead Blasting Process
Image Description: The image shows an operator using a bead blasting gun to clean a metal surface inside a blasting cabinet.
Before getting into further details, first, let’s talk about the working principle of bead blasting. It works on the high velocity and pressure flow of the spherical beads. These beads subsequently apply to the surfaces in question, giving the satin appearance to the metal surface. The shape, material, and blast size media are considerable factors that determine the process outcomes.
Step # 1. Selection of Materials for Bead Blasting
Manufacturers employ different types of materials for bead blasting. These materials are distinct in creating impacts on different surfaces.
Step # 2. High-Velocity Projection
Next, the high-velocity projection beads are applied against the surface to give it a homogeneous finish. The glass beads will create a rough, textured surface required for many tasks. The rough surface provides better adherence for painting and other coatings.
Step # 3. Bead Blasting
Manufacturers of various industries use different types of materials for bead blasting. The most typical form of beads is glass beads. The glass bead diameter is usually around 0.8 to 4mm. Besides, glass beads allow manufacturers to create a finer, smoother finish on the treated surface.
Types of Bead Blasting Materials and Their Applications
However, glass beads have no downsides since no chemical reaction is involved with their substrate. Industries like automobiles and aircraft are using bead blasting techniques to provide a finished appearance to their spare parts that consequently provide better performance and maximizes fuel efficiency.
Steel Shot
 Steel Shot for Blasting Machine
Steel Shot for Blasting Machine
Image Description: Here, the image depicts spherical steel shot media used inside an industrial blasting cabinet to polish.
To achieve better results, you need to correspond your bead to the material if the surface differs. For example, for more aggressive bead blasting, steel shots serve as a better option. Steel shot creates a textured surface that glass beads cannot achieve.
In addition, they are reusable. So, it’s a cost-effective choice for heavy-duty applications. Engineers generally use steel shots to clean large metal parts and to prepare surfaces for post-processing.
Aluminum Oxide
 Aluminum Oxide Grit
Aluminum Oxide Grit
Image Description: The image shows aluminum oxide grit used in a sandblasting cabinet to clean and roughen a metal surface before coating.
Aluminum oxide is a preferred choice for the hardware items. Since aluminum oxide is a highly durable and abrasive material, engineers choose it for cleaning and etching hard metal surfaces. Moreover, the procedure can roughen the surface enough to allow the paint or enamel to stick adequately. In addition, aluminum oxide media can be used where strong abrasion is required, such as in sandblasting operations.
Ceramic Beads
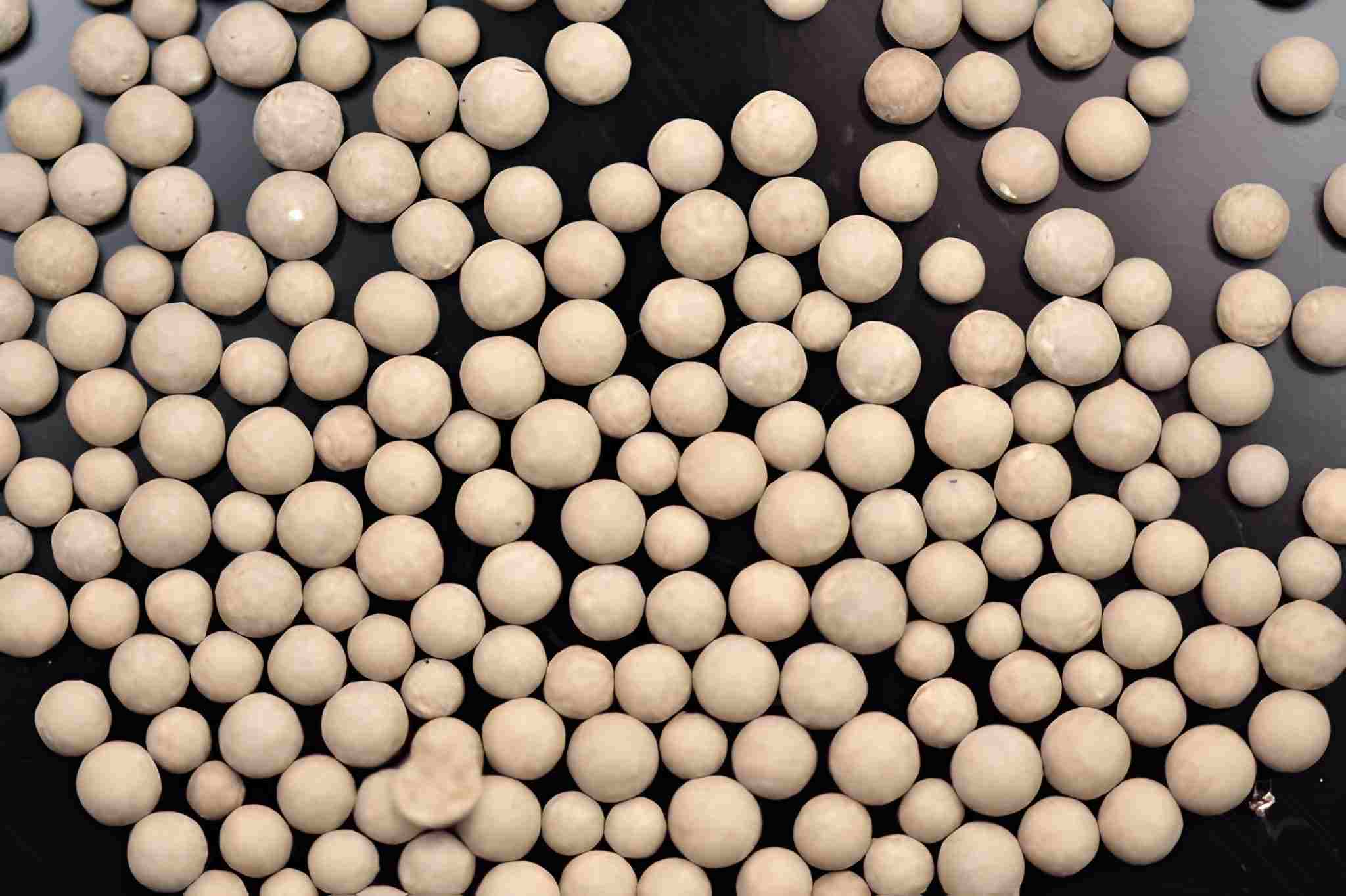 Ceramic Beads for Clean Blast
Ceramic Beads for Clean Blast
Image Description: The image shows a close-up of spherical ceramic beads, highlighting their uniform size and glossy texture.
Ceramic beads are the most frequently used media for blasting. It is normally composed of plastic or soft metals as its substrate. In addition, ceramic beads are comparatively harder than glass beads. Consequently, softer than steel shots and aluminum oxide media. This makes them ideal for creating impacts on the metal surface. The ceramic beads, moreover, provide minimal wear to the surface upon projection.
Equipment Used In the Bead Blasting Process
Design Manufacturers employ various tools and equipment for the bead blast process to obtain an aesthetic sense for the product.
1. Blast Media
Engineers usually use the media or the material for the process of recoverable blasting media. This means that it has a longer shelf life and is useful after recycling. The workers in different industries use two forms of media.
- Spherical media
- Angular media
Table 1: Comparison of spherical and angular media.
| Spherical media | Angular media |
| This is used to make the surface smooth | This is used to remove dust and rust from surfaces |
| Higher pressure reduces the media life. | Higher blast pressure increases the production |
| It gave a finish and shine to the surface | Dust and rust are collected at the end |
| Typical pressure is about 20-55 pascals. | Pressure is maintained at 20-90 pascals. |
| Glass beads have 9-12 cycles and a 10% breakdown | Ceramic has 70-90 life cycles and a 1.2% breakdown |
| Examples
● Ceramic beads ● Glass beads ● Stainless steel shots |
Examples
● Ceramic grit ● Crushed glass ● Steel grit
|
2. Bead Blaster Cabinet
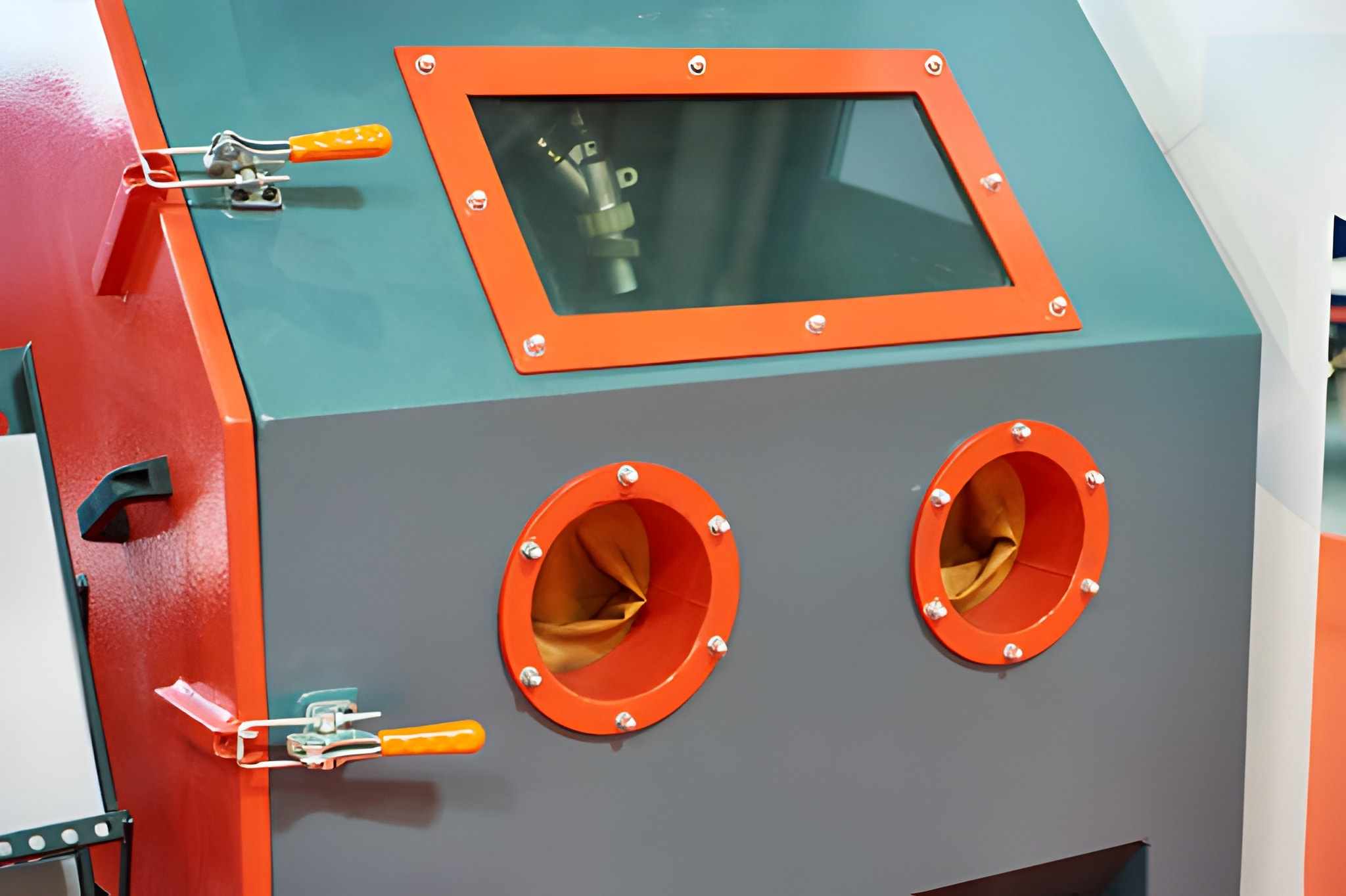 Bead Blasting Chamber
Bead Blasting Chamber
Image Description: Here, the image displays an industrial bead blasting chamber designed for precision surface finishing and dust-free operation.
Designers usually use a bead blaster cabinet made of steel to bear the high pressure. The operator places all the media and materials inside the blaster cabinet. You evaluate the strength of the cabinet legs. As long as the cabinet legs are strong enough that they won’t wobble under high-pressure operations. Besides, workers must properly seal the window of the bead blast cabinet to prevent any leakage of the bead blast media.
3. Sealing
The cabinet should have consistent sealing so there will be no exposure to dust or debris. These materials may pose health concerns. Therefore, you must check that the cabinet is sealed properly.
4. Protective Windows
The bead blaster cabinet has windows from where the operators can monitor the workpieces inside the cabinet. Glass beads used cause frosting effects that may impair vision. Therefore, the workers should use replacement windows for a clear view.
5. Bead Blaster Gun
Manufacturers, in general, use a special gun to blast media onto the object surface in question. The gun propels the abrasive material onto the surface with high pressure. You can use two types of guns in this process:
- Handheld Gun: The machinists can easily handle this portable and small gun, which exerts less pressure.
- Benchtop Gun: A Benchtop gun attaches to a surface, is larger, and can bear very high pressure.
6. Blasting Glove
The bead blasting process requires complete safety equipment for the system’s workers. Gloves for this process provide safety as well as provide grip for proper functioning. This technique in industries uses abrasive material to remove the rust and make the surface smooth; therefore, exposure to the beads can cause injury and impact the worker. Wearing gloves reduces the potential cause of injury to the hands.
Bead Blasting vs Sandblasting: How They Differ?
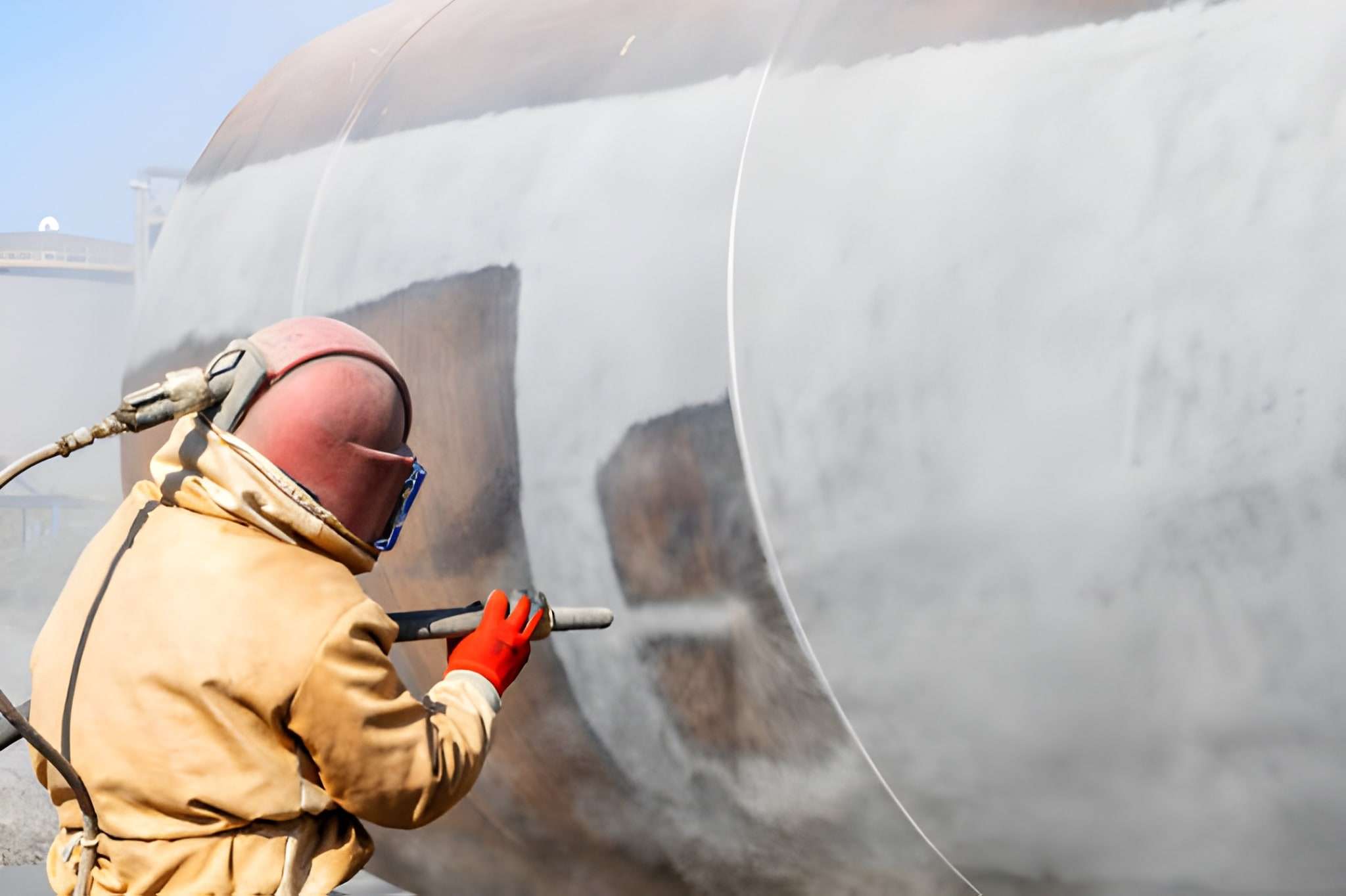 Sand Blasting
Sand Blasting
Image Description: The image shows an operator wearing protective gear while handling a blasting gun.
However, both operations, bead blasting vs sandblasting, are used interchangeably. But they are relatively different. Let’s compare each process in detail:
Table 2: Comparison between Bead Blasting vs Sandblasting.
| Bead Blasting | Sandblasting |
| Media Used: Glass, Ceramic, plastic, or steel beads for blasting. | Media Used: Workers use silica and sand for the procedure. |
| Employs high-velocity projection of a bead onto the substrate surface. | The process is similar; the difference is only in the media used. |
| slower but gentler procedure | Faster procedure |
| The procedure does not affect the metal surface, as the beads are much smoother. | Sand particles are relatively harder and can etch the metal surface. |
| Dust and rust may cause breathing difficulties for people working in that field. | Health concerns like silicosis are very common using this method |
| The inner surface of the metal remains intact | Harshness can affect the metal’s inner surface. |
What Are The Typical Functions of Bead Blasting?
There are three primary functions of bead blasting. These include cleaning, texturing, and finishing. Let’s briefly few details of each:
- Cleaning: Cleaning refers to the removal of rust, dust, and paint from a surface in question.
- Finishing: Deburring, peening, polishing, and cosmetic finishes are all classified as the same bead blasting operations. Besides, preparing the part surfaces for the next finish steps is also a part of this phase.
- Texturing: Texturing is defined as the process of making the surface of metal pieces satin, matte, or textured in final touch-ups.
Application Area of Bead Blasting in Industries
Different industries are using this process for making the material surface matte or finish. Some of them are as follows:
Aerospace industry
 Bead Blast Massive Machine Part
Bead Blast Massive Machine Part
Image Description: The image shows a massive machine part suspended by a hoist as it is bead blasted from multiple angles in a production facility.
In the aerospace sector, normally deburring process is normally used. It allows aircraft part makers to remove sharp edges and make metal surfaces burr free. A few examples of parts/products that bead blasted include aircraft engine components, such as turbine blades and compressors.
Automotive industry
The automobile industry uses a cosmetic finish to keep spare parts satin-looking. It protects the surface from rust and thermal damage. The process allows automakers to treat engine parts, transmission components, and brake parts.
Medical industry
The medical industry normally textures aluminum using a bead blasting procedure. Typical examples include surgical instruments, orthopedic implants, and dental parts.
What Are The Benefits of Using Bead Blasting?
Bead blasting is highly regarded in several manufacturing industries since it allows users to reuse media. Some of the common benefits include:
Effective Cleaning and Surface Preparation
Design manufacturers use bead blasting to precisely clean and prepare surfaces to last longer. Glass beads or sand beads are typically involved and projected by an electrostatic gun. It allows the operator to remove oil, dust, and contaminants from delicate surfaces. Therefore, the technique dominated other conventional techniques since it allows the clean and even intricate design components. Besides, other abrasive techniques might cause damage and distortion.
Uniform Finish and Texture
As mentioned above, the primary reason to employ the bead blasting process is to attain the desired texture of the surface and make it more compatible with painting. Besides, it removes the micro-level defects that could trap moisture and debris.
Adaptability
Bead blasting enables manufacturers to choose from a variety of options for blasting media according to their requirements and parts’ material. It is effective to apply to any type of material, including plastic, ceramic, and glass. In addition, it entertains even more delicate and large-sized parts and makes the satin, matte, and uniform. Thus, it is a popular choice across diverse industries, such as manufacturing, electronics, and medical devices.
Economical and Environmentally Friendly
Many Industries exploit the bead blast process because of its scale economy. For example, you can reuse abrasive bead media after the cycle completion. Besides, the process generates minimal heat, which is less likely to damage heat-sensitive materials. The glass media is lead-free, making it suitable for every environment.
Effective Tips for the Best Bead Blast Finish
Many factors can influence the final appearance of the bead-blasted product. Manufacturers can use various tips to make the process flawless.
Tip # 1: Specify Grit Size and Texture
Generally speaking, fine glass beads provide a smooth and satin surface. While coarse glass beads create a rougher texture. Steel shots are ideal for polishing and removing undesired textures. Each type of media is engineered for different uses. So, it’s recommended to choose the grit size based on your needs. In addition, lower grit may give you results in coarser particles, while higher grit yields finer finishes.
Tip # 2: Avoid Tight Surface Roughness Callouts
In general, it’s quite difficult to meet the tight surface roughness callouts. For smoother parts, try to avoid a roughness range lower than 32 µin Ra. Moreover, be aware that achieving precision in surface roughness may not always be easier with bead blasting.
Tip # 3: Add Masking Notes for Critical Features
Certain areas on the product do not require bead blasting. In that case, use a masking note to protect those areas, such as O-ring grooves, sealing surfaces, and small-pitch features, during the process.
Tip # 4: Keep The Pressure Lower
A pressure of 50 PSI is optimal for maintaining the shape and texture of the beads. Also, it effectively removes dust or debris with relative ease.
Tip # 5: Removing Oxides Before Bead Blasting
While bead blasting aluminum, it is important to scrape off the rusted layer with a sharp tool to make the most out of this procedure. It can provide better results in the finish after getting a rust-free surface.
What Are The Limitations of Bead Blasting?
Even though the bead blasting process has enormous benefits. But, alongside, it has certain drawbacks. For instance.
- The treatment consumes more time to achieve the desired surface finish.
- Industrial bead blasting needs professional supervision because, in most cases surface can become uneven due to minor fluctuations in process parameters.
- The Equipment used in the process requires proper cleaning and maintainance.
- In some cases, the surface wears down quickly due to frequent bead blasting.
Conclusion
In conclusion, bead blasting is a highly effective and adaptable surface treatment. It’s highly practiced in aerospace, automotive, and medical fields. In addition, it offers advantages like cost-effectiveness, recyclability, and environmental friendliness.
However, to achieve optimal results, manufacturers must carefully select the right media, pressure, and grit size. Furthermore, adequate masking, preparation, and equipment checkover are vital for achieving a flawless outcome. Despite all these benefits, it poses a few limitations to the process. Manufacturers need to consider how much time production will take and make sure experts are involved to avoid mistakes and imperfections. For expert bead blasting services, consult our engineers for professional advice!
FAQs
Q1. What media type can be used for the bead blasting process?
The media used included glass, ceramic, and many other materials. These help provide the desired results on the surface.
Q2. What are the Safety precautions that I should take while using a bead blasting process?
Use PPE (Personal Protective Equipment) while operating bead blasting machines and media. The process should take place in a sealed environment to protect the product from dust and debris.
Q3. How bead blasting is different from sandblasting
In sandblasting, silica is a medium of treatment instead of glass for the procedure. This process of sandblasting is quite harsh compared to glass bead blasting.
Q4. Which metals can be effectively?
Manufacturers mainly use blasting techniques to treat metals like aluminum, brass, copper, titanium, and nickel.